* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Osteoporosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
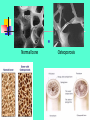
OSTEOPOROSIS IACOVOS ANTONIOU GROUP 35 (2010) Osteoporosis “A systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration, with a consequent increase in bone fragility with susceptibility to fracture.”* One in 2 women and One in 8 men over 50 will have an osteoporosis related fracture. The estimated cost for osteoporotic and associated fractures is 38 million a day! Risks for Osteoporosis In young women • Low calcium intake • Low body weight • Limited exercise • Hypoestrogenism In others • Menopausal/postmenopausal status—without HRT • Cigarette smoking • Low-trauma fractures • Hyperparathyroidism • Chronic corticosteroid use Normal bone Osteoporosis Bone Health Bones are living tissue, they provide structural support, protect vital organs and store calcium. Until age 30, we store and build bone effectively. As part of the aging process, bones begin to break down faster than they are formed. Accelerates after menopause. Estrogens are the hormones that protects against bone loss. Prevention Building strong bones in childhood and adolescence is the best defense. A balanced diet rich in calcium and Vitamin D Weight bearing exercise A healthy lifestyle with no smoking or excessive alcohol intake. Bone density testing and medication when appropriate. Calcium Is needed for heart muscles, and nerves to function properly. Inadequate amounts contribute to osteoporosis. Appropriate calcium intake falls between 1000 and 1300 mg a day. Calcium Increase calcium: Consume calcium rich foods such as, low-fat milk, cheese, broccoli, and others. Calcium supplement, if dietary calcium consumption is inadequate How to get enough Calcium every day! Follow the Food Guide Pyramid for Dietary Calcium Sources Dairy – low fat yogurt, skim milk, cheese, chocolate pudding, ice milk, ice cream or frozen yogurt. Protein – tofu, sardines, salmon Vegetables – turnip greens, Bok Choy, Broccoli, collard greens Other foods: vegetable lasagna, cheese enchilada, cheese pizza, calcium fortified orange juice. Vitamin D Is needed for your body to absorb calcium. Comes from 2 sources: the sun and Fortified dairy products, egg yolks, saltwater fish, and liver. Need 400–800 IU a day. Vitamin D Medications There is no cure, but several medications have been approved. Each stops or slows bone loss, increases bone density, and reduces fracture risk. Estrogen Replacement, Alendronate, raloxifene and risedronate are prescribed to prevent and treat the disease. Bone-Building Checklist Maintain a calcium rich diet. Get plenty of vitamin D Engage in weight-bearing exercise Don’t smoke and limit alcohol intake Consider Hormone Replacement or other medications if you are at risk. Estrogens Estrogens include the natural hormones as well as semi-synthetic and synthetic (stilbene) agents Estrogens are used as hormone-replacement therapy (menopause), in oncology and as contraceptives Most estrogen in the female is produced in the ovaries by the theca interna and the granulosa cells of the follicles Actions of estrogens on sexual organs (primary and secondary sexual characteristics) ovaries : stimulate follicular growth; small doses cause an increase in weight of ovary; large doses cause atrophy uterus: endometrial growth vagina: cornification of epithelial cells with thickening and stratification of epithelium cervix: increase of cervical mucous with a lowered viscosity (favoring sperm access) Actions of estrogens Development and maintenance of internal (fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina), and external genitalia skin: increase in vascularization, development of soft, textured and smooth skin bone: increase osteoblastic activity electrolytes: retention of Na+, Cl- and water by the kidney cholesterol: hypocholesterolemic effect Natural estrogens Conjugated estrogenic substances: an amorphous preparation containing water soluble conjugated forms of mixed estrogens from the urine of pregnant mares (Premarin, Cenestin - synthetic conjugated estrogens) estradiol : oral : Estrace transdermal: Climara, Alora, Vivelle, Vivelle-Dot, Estraderm, FemPatch Natural estrogens estrone: Kestrone 5 (injectable only) esterified estrogen (75–85% sodium estrone sulfate and 6–15% sodium equilin sulfate) Estratab; Menest estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate) Ogen; Ortho-Est Natural estrogens Sustained-release injectables: estradiol valerate in oil (Delestrogen; Valergen) estradiol cypionate in oil (depGynogen; DepoGen) duration of action from 3 to 8 weeks esterified at C-17 hydroyl group