* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Decision Support Systems and Marketing Research
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Field research wikipedia , lookup
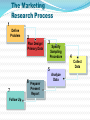
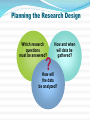
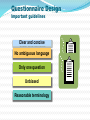
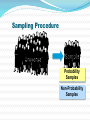
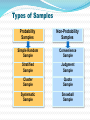
Key Concepts What is MDSS? Marketing Decision Support Systems An interactive, flexible computerized information system that enables managers to obtain and manipulate information as they are making decisions. DSS System Characteristics Interactive Flexible Discovery-Oriented Accessible Marketing Decision Support Systems Database Marketing The creation of a large computerized file of customers’ and potential customers’ profiles and purchase patterns. The key tool for successful one-to-one marketing. Marketing Decision Support Systems What is Marketing Research and Why it is Important Define marketing research and explain its importance to marketing decision making The Role of Marketing Research Marketing Research The process of PLANNING, COLLECTING, and ANALYZING data relevant to a marketing decision. Marketing Research Studies: What issues are often investigated? Products Uses Advertising Awareness Prices Familiarity Packages New concepts Names and Logos Traffic patterns Services Wants Buying habits Needs Colors Politics The Role of Marketing Research Descriptive Gathering and presenting factual statements Diagnostic Explaining data Predictive “What if?” When Should Marketing Research Be Conducted? Where there is a HIGH level of UNCERTAINTY When VALUE of research information exceeds the COST of generating the information Management Uses of Marketing Research Improve the quality of decision making Trace problems Focus on keeping existing customers Understand the marketplace Alert them to marketplace trends Gauge the value of goods and services, and the level of customer satisfaction The Marketing Research Process 1 Define Problem 2 Plan Design/ Primary Data 3 Specify Sampling Procedure Collect Data 5 6 Prepare/ 7 Follow Up Present Report 4 Analyze Data Marketing Research Marketing Research Problem Determining WHAT INFO IS NEEDED and HOW that information can be obtained efficiently and effectively. Marketing Research Objective The specific INFO needed to SOLVE A MARKETING RESEARCH PROBLEM; the objective should provide insightful decision-making information. Management Decision Problem A broad-based problem that requires marketing research in order for managers to take proper actions. Secondary Data Secondary Data Data PREVIOUSLY COLLECTED for any purpose other than the one at hand. SOURCES of Secondary Data Where the info can be accessed Internal Corporate Information Government Agencies Trade and Industry Associations Business Periodicals News Media Advantages of Secondary Data Saves time and money if on target Aids in determining direction for primary data collection Pinpoints the kinds of people to approach Serves as a basis of comparison for other data Disadvantages of Secondary Data May not give adequate detailed information May not be on target with the research problem Quality and accuracy of data may pose a problem The New Age of Secondary Information: The Internet 1 Analyze your topic 2 Test run a word or phrase in a search engine 3 Learn as you go and vary your approach 4 Don’t bog down in strategy that doesn’t work 5 Go back to earlier steps better informed Planning the Research Design Which research questions must be answered? ? How and when will data be gathered? How will the data be analyzed? Primary Data Primary Data Information collected FOR THE FIRST TIME. Can be used for solving the particular problem under investigation. Advantages of Primary Data Answers a specific research question Data are current Source of data is known Secrecy can be maintained Disadvantages of Primary Data Disadvantages are usually offset by the advantages of primary data. Expensive “Piggybacking” may confuse respondents Quality declines if interviews are lengthy Reluctance to participate in lengthy interviews Survey Research Survey Research The MOST POPULAR TECHNIQUE for gathering primary data in which a researcher interacts with people to obtain facts, opinions, and attitudes. Forms of Survey Research In-Home Interviews Mail Surveys Mall Intercept Interviews Executive Interviews Telephone Interviews Focus Groups Forms of Survey Research Mall Intercept Interview Survey research method that involves INTERVIEWING PEOPLE in the common areas of SHOPPING MALLS. Executive Interview A type of survey that involves INTERVIEWING EXECUTIVES AT THE OFFICES concerning industrial products or services. Forms of Survey Research Focus Groups Seven to ten people who participate in a GROUP DISCUSSION led by a moderator. Questionnaire Design How questions are formatted Open-Ended Question An interview question that encourages an answer phrased in RESPONDENT’S OWN WORDS. Closed-Ended Question An interview question that asks the respondent to MAKE A SELECTION from a LIMITED LIST of responses. ScaledResponse Question A closed-ended question designed to MEASURE THE INTENSITY of a respondent’s answer. Questionnaire Design Important guidelines Clear and concise No ambiguous language Only one question Unbiased Reasonable terminology Observation Research Observation Research A research method that relies on three types of OBSERVATIONS: people watching people people watching an activity machines watching people Observational Situations Situation Example People watching people People watching phenomena Machines watching people Machines watching phenomena MYSTERY shoppers in a supermarket Observer at an intersection counting traffic VIDEO cameras recording behavior Trafficcounting MACHINE monitoring traffic flow Ethnographic Research Ethnographic Research The study of human behavior in its NATURAL CONTEXT; involves observation of behavior and physical setting. The Sampling Procedure Sample A SUBSET from a large population. Universe The POPULATION from which a sample will be drawn. Sampling Procedure Universe Sample Probability Samples Non-Probability Samples Types of Samples Probability Samples Non-Probability Samples Simple Random Sample Convenience Sample Stratified Sample Judgment Sample Cluster Sample Quota Sample Systematic Sample Snowball Sample Probability Samples Probability Sample A sample in which every element in the population has a known statistical likelihood of being selected. Random Sample A sample arranged so that every element of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Nonprobability Samples Nonprobability Sample Any sample in which little or NO ATTEMPT is made to get a representative cross-section of the population. Convenience Sample A form of non-probability sample using respondents who are CONVENIENT or READILY ACCESSIBLE to the researcher. Types of Errors Measurement Error Error when there is a DIFFERENCE between the information desired and the information provided by research Sampling Error Error when a sample somehow DOES NOT REPRESENT the target population. Frame Error Error when a SAMPLE drawn from a population DIFFERS from the target population. Random Error Error because the selected sample is an IMPERFECT REPRESENTATION of the overall population. Field Service Firms Provide: Focus group facilities Mall intercept locations Test product storage Kitchen facilities Retail audits Analyzing the Data CrossTabulation A method of analyzing data that lets the analyst look at the responses to one question IN RELATION to the responses to one or more other questions. Preparing and Presenting the Report What the report should contain Concise statement of the research objectives Explanation of research design Summary of major findings Conclusion with recommendations Following Up Were the recommendations followed? Was sufficient decision-making information included in the report? What could have been done to make the report more useful to management? Steps in a Marketing Research Project The Internet & Marketing Research Explore the the profound impact of the Internet on marketing research Impact of the Internet Allows better and faster decision making Improves ability to respond quickly to customer needs and market shifts Makes follow-up studies and tracking research easier Slashes labor- and time-intensive research activities and costs Advantages of Internet Surveys Rapid development, Real-time reporting Reduced costs Personalized questions and data Improved respondent participation Contact with the hard-to-reach Uses of the Internet by Marketing Researchers Administer surveys Conduct focus groups Other types of marketing research Internet Samples LO4 Unrestricted Internet Sample A survey in which ANYONE with a computer and modem can fill out the questionnaire. Screened Internet Sample An Internet sample with QUOTAS based on desired sample characteristics. Recruited Internet Sample A sample in which respondents are PRE-RECRUITED and must QUALIFY to participate. Process for Online Focus Groups 1. Build a database of respondents via Web site screening questionnaire 2. Identify qualified individuals via e-mail 3. Develop a discussion guide 4. Moderator runs group by typing in questions online for all to see 5. Environment is similar to a chat room 6. Firm captures the complete text of the focus group Types of Online Focus Groups Real-time online focus groups Time-extended online focus groups Advantages of Online Focus Groups Speed Cost-effectiveness Broad geographic scope Accessibility Honesty Role of Blogs in Marketing Research Refined technologies allow companies to mine data available in Internet blogs. Companies can identify the most influential bloggers and learn exactly what they are saying (and how they are saying it). Other Uses of the Internet by Marketing Researchers Distribution of requests for proposals (RFPs) and proposals Collaboration between client and research supplier Data management and online analysis Publication and distribution of reports Viewing of presentations of marketing research surveys Impact of the Internet on Marketing Research Scanner-Based Research Explore the growing importance of scanner-based research Scanner-Based Research A system for gathering information Scanner-based Research from a single group of respondents by CONTINUOUSLY MONITORING the advertising, promotion, and pricing they are exposed to and the things they buy. BehaviorScan InfoScan Competitive Intelligence Competitive Intelligence An intelligence system that helps managers assess their competition and vendors in order to become more efficient and effective competitors. Sources of Competitive Intelligence Internet UCC Filings Company Salespeople Suppliers Experts Periodicals CI Consultants Yellow Pages Government Agencies Trade Shows



























































![CH08 rev[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008068136_1-f4fa6bc41e26e303aa806d558864a5a9-150x150.png)






