* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Land Form Patterns: Tectonic Faults
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
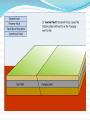
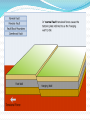
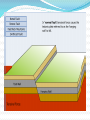
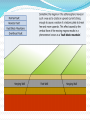
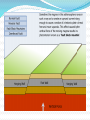
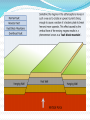
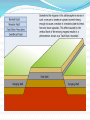
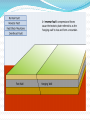
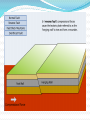
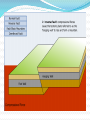
Unit 1: Land & Water Forms World Geography 3200/3202 Outcomes In this lesson you will: 1.1.6 Explain how tensional forces create a normal fault. (k) 1.1.7 Explain how compressional forces create reverse and overthrust faults. (k) This lesson corresponds to the information contained in the "Mountains Formed by Faulting" section found on page 14 of your text. Fault Lines Fault lines are basically great cracks in the earth’s crust created when plates are compressed against each other. The break or crack may be slight or may run deep into the Earth’s crust The length of the fault may be short or may extend hundreds of kms. Faulting Faulting is instrumental in mountain building Geologists have analyzed the precise ways in which plates are changed by faulting & have developed four main types of mountains 1. Normal Fault Mountains Caused by: tensional forces. Occurs when: A plate on one side of the fault drops down lower than the plate on the other side Fault Block Mountains Sometimes two normal faults occur parallel to each other In some cases the broken plate between the faults drops as the broken plates move away from each other forming a rift valley In case when many layers of the Earth's crust are moved vertically upward between two parallel fault lines, Fault Block Mountains result. The vertical force is caused by the Earth's internal pressure. Reverse Fault Mountains When simple rock layers around a fault push against each other instead of pulling away, one block can be pushed up over the other This results in the creation of a Reverse Fault Mountain caused by compressional forces where plates move together at the fault. Overthrust Faults when the plate that suffers the fault has already undergone folding, & its folded layers are then pushed up & thrust over layers on the fault’s other side, an Overthrust Fault occurs. Faulting: A Review Q. What name is given to large cracks in the earth's crust? A. FAULT LINES Q. What name is given to faults formed by tensional forces? A.NORMAL FAULTS Q. What name is given to faults formed by compressional forces? A. REVERSE FAULTS Q. How do overthrust faults differ from regular reverse faults? A. THEY WERE FOLDED BEFORE FAULTING