* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A brief introduction to Quantum computer Alri Moore`s law the
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot cellular automaton wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
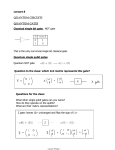
A brief introduction to Quantum computer Alri Moore's law the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit has doubled approximately every two years ——- Gordon E. Moore, the co-founder of Intel speed and computing capacity physical limits atomic level quantum theory classical computer ——> quantum computer? Qubit a linear superposition of basis states both states at the same time two-state quantum-mechanical system Quantum entanglement system as a whole one particle of an entangled pair "knows" what measurement has been performed on the other, and with what outcome Faster-than-light Quantum mechanics not true communication two observers in different locations see the same system simultaneously Energy and computing Landauer's principle: the erasure of n bits of information must always incur a cost of n k T ln(2) in thermodynamic entropy erasure of information — necessary? Reversible computing the relation of the mapping from states to their successors must be one-to-one Toffoli gate CCNOT gate "controlled-controlled-not" gate any reversible circuit can be constructed from Toffoli gates 3-bit inputs and outputs : if the first two bits are set, it inverts the third bit, otherwise all bits stay the same Toffoli gate The Toffoli gate is reversible (but the Toffoli' used above is not). This means that any computation did with it can be undone. This is: (a,b,c)=Toffoli(Toffoli(a,b,c)) Universality and Toffoli gate Boolean functions: OR, AND,NOT gates NOR gates NAND gates Toffoli gate NAND(a,b)=Toffoli′(a,b,1) NOT(x)=Toffoli′(1,1,x) AND(a,b)=Toffoli′(a,b,0) basic quantum computers that can perform certain calculations D-Wave Systems 512-qubit D-Wave Two quantum computer new era References https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore%27s_law https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Qubit#Bit_versus_qubit https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_entanglemen t http://www.technologyreview.com/view/422511/th e-fantastical-promise-of-reversible-computing/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toffoli_gate http://www.dwavesys.com/quantum-computing Thank you!