* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
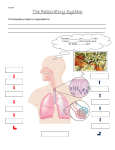
Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Nose ● Primary organ from which air enters and leaves the body ● Mucus and Cilia lining help trap unwanted particles from entering the body ● Humidifies and moistens air ● Septum divides the nose into two parts ● One part is for respiration ● The other is for smelling Pharynx ● Tubular structure between the nasal and oral cavity that allows air to travel from mouth to lungs ● Throat ● Three parts ● ● ● ● Nasopharynx ● Oropharynx ● Laryngopharynx Contains connective muscles that prevent us from swallowing air Epiglottis: flap of tissue that channel air to the lungs and food to the esophagus Isthmus: Connects the oral and nasal portions, allows humans to breathe through the nose or mouth Larynx ● “Voice box” ● Passageway for air to the lungs ● Source of vocalization ● Hyoid bone and cartilage, help regulate airflow Bronchi ● Allows air to enter the lungs ● Two parts ● Right main bronchus is shorter and wider than the left ● Right bronchus is subdivided into three parts ● Left bronchus is divided into two parts Lungs ● Left lung is divided into superior and inferior lobe ● Right lung is divided into superior, middle, and inferior lobe ● Main job is respiration ● Take oxygen from the atmosphere and put it into blood ● Take CO2 from blood and breathe it into the atmosphere Alveoli ● 600 million alveoli ● Grape-like trees at the end of the “respiratory tree” ● Gas exchanges take place here ● Some effort to inflate the sacs ● Little to no effort to deflate the sacs Diaphragm ● Muscular structure between the thoracic and abdominal cavities ● When air comes in, the diaphragm expands and opens up the chest cavity allowing more room for air to enter the lungs Epithelial Tissue ● Lines the surface and cavities of organs ● Simple squamous epithelial tissue makes up the alveoli ● ● Easy to diffuse oxygen into the bloodstream Stratified squamous epithelial tissue found as a layer for alveoli ● Easy diffusion ● Protective layer against airborne pathogens/toxins ● Simple: Single cell layer ● Stratified: Composed of multiple cell layers Other Tissues ● ● ● Nerve tissue ● Reacts to stimuli ● Conducts impulses Muscle tissue ● Soft tissue that composes muscle ● Smooth muscle tissue ● Controls slow, involuntary movement ● Contracts and relaxes organs Connective tissue ● Maintains form of body ● Provides cohesion and internal support, as well as connectivity Epithelial Cells ● Lines respiratory tract ● Moistens and protects airways, serves as a barrier for pathogens and foreign particles ● Ciliated cells ● ● Very long epithelial cells ● Specialized cilia attachments Goblet cells ● Secrete mucins to create mucus Red Blood Cells ● ● Delivers oxygen to parts of the body through the circulatory system Hemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues in the body, and carbon dioxide from back to the lungs Other Cells ● ● Alveolar Cells ● Type I: Line the alveoli. Important for gas exchange ● Type II: Scattered among the Type I cells, secrete ingredients for a surfactant to coat the alveoli Club Cells ● Nonciliated cells ● Secrete a serous product that helps create a surfactant to protect the bronchial lining. ● Found in the bronchiolar epithelium Hormones ● Essential for cell communication ● Thyroxine: Produced by thyroid gland; facilitates respiration ● Carbonic anhydrase: Combines carbon dioxide with water to form carbonic acid to transfer carbon dioxide through the body ● Angiotensin (converting enzyme): Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II to contract blood vessels ● Others: Hypothalmic, neuropeptides, estrogen, testosterone, leptin, dopamine Chemoreceptors ● Receptors in the medulla oblongata detect changes in the pH levels of the blood. ● If not enough oxygen is being taken in, the CO2 level of the blood rise, and the blood becomes more acidic. ● This triggers an increase in nerve impulses that stimulate the diaphragm which increases lung ventilation and brings the CO2 blood levels to normal. Other Features ● ● Cilia ● Microscopic, hair-like structures that extend from the surface of cells ● Rhythmic waving or beating motion ● Keep the airways clear of mucus and dirt, blocking pathogens and allowing for easier breath Mucus ● Protects the mucous membranes ● Maintain epithelial moisture ● Traps particulate material and pathogens moving through the airway Work Cited ● "Anonymous." SpringerReference (n.d.): n. pag. Springer. Web. 4 Mar. 2016. ● "The Human Body @ NNHS." Specialized Cells and Structures of the Respiratory System -. NNHS, n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "RESPIRATORY SYSTEM." Respiratory Sys. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Chapter 23. The Sensory System." Introduction to Healthcare for Interpreters and Translators (2013): 233-42. Web. ● "Respiratory System: Level of Organization - Sam's Science Project."Respiratory System: Level of Organization - Sam's Science Project. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Epithelial Cells." Simple Squamous Epithelium. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Epithelial Cells." Stratified Epithelium. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Nervous Tissues." Nervous Tissue. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Muscle Tissues." Muscle Tissue. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● Fawcett, Don W. "Connective Tissue." Encyclopedia Britannica Online. Encyclopedia Britannica, n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica. "Pharynx." Encyclopedia Britannica Online. Encyclopedia Britannica, n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Functions of Organs in Respiratory System | MD-Health.com." Functions of Organs in Respiratory System | MD-Health.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016. ● "Diaphragm in Respiratory System." InnerBody. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 Mar. 2016.