* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multicellular Organisms - Hicksville Public Schools
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
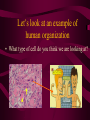
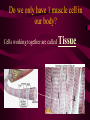
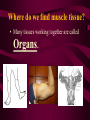
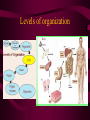
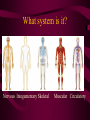
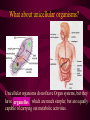
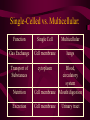
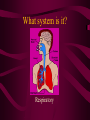
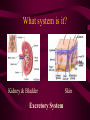
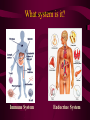
Aim: How is life organized? LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION • What does the word, organize, mean? • To put into a certain order • Given the following items, how would you organize them and why? • • City, state, country, continent • Why? It goes from small to big Why do we need to organize in our lives? So things can efficiently work together Why do living things need to be organized? • The twelve organ systems of the human body need to work together to maintain homeostasis _________. • What is the basic unit of all life? CELLS Let’s look at an example of human organization • What type of cell do you think we are looking at? Do we only have 1 muscle cell in our body? Cells working together are called Tissue. Where do we find muscle tissue? • Many tissues working together are called Organs. How can we combine the different muscular organs? • Many organs working together make up an organ systems. ORGANISM Organisms are comprised of many integrated organ systems that work together to maintain a constant stable internal environment. Multicellular Organisms Can you put these in order? A Organ system B Tissue C Organism D E Cell Organ Levels of organization What system is it? Nervous Integumentary Skeletal Muscular Circulatory What about unicellular organisms? Unicellular organisms do not have Organ systems, but they have __________ organelles which are much simpler, but are equally capable of carrying out metabolic activities. What is the overall goal of our organ systems? The organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis. In other words, the organ systems maintain an internal stability despite an always changing environment. Single-Celled vs. Multicellular: Function Gas Exchange Transport of Substances Nutrition Excretion Single Cell Multicellular Single-Celled vs. Multicellular: Function Single Cell Multicellular Gas Exchange Cell membrane lungs Transport of Substances cytoplasm Nutrition Blood, circulatory system Cell membrane Mouth/digestion Excretion Cell membrane Urinary tract What system is it? Respiratory What system is it? Digestive What system is it? Kidney & Bladder Excretory System Skin What system is it? Immune System Endocrine System ATOM ATOMS ARE THE SMALLEST UNIT OF MATTER THAT PARTICIPATE IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS. Examples: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Carbon MOLECULES Molecules are two or more atoms that are chemically combined. Can you guess what this molecule is? Hint: It is the most important molecule on earth. What system is it? Male Reproductive What system is it? Female Reproductive