* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science OGT Review
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Milankovitch cycles wikipedia , lookup
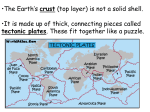
Science OGT Review Earth Science Content Standard: Earth and Space Science Benchmarks: Explain how evidence from stars and other celestial objects provide information about the processes that cause changes in the composition and scale of the physical universe. Explain that many processes occur in patterns within the Earth’s systems. Explain the 4.5 billion year history of Earth and the 4 billion year history of life on Earth based on observable scientific evidence in the geologic record. Describe the finite nature of Earth‘s resources and those human activities that can conserve or deplete Earth’s resources. Explain the processes that move and shape Earth’s surface Summarize the historical development of scientific theories and ideas, and describe emerging issues in the study of Earth and space science. Earth Science There are four areas of study that contribute to Earth Science Geology Astronomy Hydrology Meteorology The Big Bang Theory Explosion 13.7 billions years ago Galaxies are moving away from central location Red-shift- the light most galaxies gives off is close to the red end of the spectrum because energy weakens as it is stretched out. How is a star formed? Nebula- dust and gas get pulled together by gravity in space. Extreme heat is produced, causing nuclear fusion, which causes hydrogen protons to join together producing the massive energy just as our sun does. The nebula depending on the size, becomes a massive star or a low mass star. The Lifecycle of Stars The Life Cycle of a Star Main sequence stars convert hydrogen to helium in their cores. When the star runs out of hydrogen, the helium can be changed into heavier elements. The cores of the stars shrink and their surfaces expand and become cooler. Galaxies Large group of stars; billions in the universe. Our solar system- sun, Earth and 8 other planets belong to the Milky Way Galaxy. Spiral, Elliptical & Irregular Galaxies The Planets Does the sun revolve around the earth, or does the earth revolve around the sun? What causes all the planets, sun and the moon to not come crashing down on us? Law of Universal Gravitation The planets revolve around the sun due to gravity! Newton proposed between any two objects there is attraction that is proportional to the masses of the objects and the distances between them. In English: the more mass an object has, the stronger gravity pulls on the object with less mass than itself. For example, Earth has more mass than our moon, this is why the moon revolves around our Earth. The Reason We Have Night & Day The earth rotates on its axis which brings different parts of the earth in contact with the sun at certain times. The reason the sun appears to “rise in the east” is because that’s the way our earth rotates, bringing the eastern part of the U.S. in contact with the sun first. FYI- 1 day is 1 rotation of the Earth. 1 year is 1revolution of the Earth around the sun. Tools Used By Astronomers Telescopes Spaceship Satellites Probes Rover Quiz Answer the following questions Quiz 1. Name 4 areas of study that contribute to Earth Science. What does red-shifting mean? How is a star formed? What is the core of the sun made of? Name 3 types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is Earth from? How many planets are recognized? Does the sun revolve around the earth or does the moon revolve around the earth? What causes night and day on earth? What are tools used by an astronomer? Seasons Earth is tilted as it revolves around the sun which allows various places to have a certain weather during the seasons. 4 Seasons Seasons Cont. During winter for Cleveland and other places in the Northern Hemisphere, we are tilted out of contact with these hottest rays from the sun. This is why it is cold. Places along the equator are hot year round because they are in direct contact with the sun’s hottest rays or very close to them When the Northern Hemisphere is having winter, the Southern Hemisphere is having summer. This is because the Earth’s tilt brings the S. Hemishere in contact with the hottest direct rays. Places along the equator are warm year round because the hot direct rays never move far from the equator. Places close to the N. & S. Pole never get the sun’s direct hot rays. This is why its never warm in these areas. The Moon Solar Eclipse Occurs when the moon either partially or completely blocks the sun from the Earth’s view. The last total eclipse was the solar eclipse of July 11, 2010. The next will be the solar eclipse of November 13, 2012. Lunar Eclipse Plate Tectonics Theory Theory that the Earth’s crust is made up of many plates that are floating on top of the Earth’s mantle layer that is molten liquid rock. These plates interact with each other in many ways… 1) When plates slide past each other creating friction, earthquakes occur. 2) When Earth’s plates collide and push up they can create mountain ranges 3) Magma from mantle can erupt passed space between 2 plates or melt through a soft crustal plate. 4) The crustal plates sit on the mantle layer of the Earth. The mantle is liquid hot rock that convection currents. These convection currents push the plates around causing continents to drift and seafloors to spread. Plates & Boundaries http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynami cearth/plate.html The Continental Drift Theory Alfred Wagener proposed that at one time all continents joined together in a single land mass. Evidence to support theory is that 1) identical fossils of an animal were found on different continents 2) identical rock layers were found on many continents 3) continents fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. Cross Section Rock sediments get laid down where the oldest rock is at the bottom. Which layer is the youngest? Due to plates moving, sometimes layers of the earth get folded or faulted. Fossil Fuels Fossil layers are a source of fossil fuels Organisms turned into carbon which we use as fuel, including gasoline, oil and coal. Nonrenewable Resources- cannot be ever replaced or renewed; took millions of years to form. Renewable Resources- can be renewed and replaced. Sunlight, water power, wind, wood, crops are all renewable Sunlight never runs out! Crops and wood can be grown constantly What is a downside to fossil fuels? They will run out one day soon They cause Global Warming Global Warming Global warming is the planet becoming warmer throughout the years. Greenhouse Effect- The Earth has an insulation layer of CO2 in its atmosphere that helps keep warmth from the sun. The layer is thin enough to let some heat escape so our planet does not get too hot. When fossil fuels & wood are burned they give off carbon dioxide (CO2) which causes the insulation layer to be too thick so not too much heat is trapped not being allowed to escape. This causes Global Warming! What Can We Do? We can use clean alternative energy sources (non carbon dioxide producing sources) We can conserve resources Recycle Car pool Riding a bicycle instead of driving Use public transportation Turn off water and electricity when not in use Conservation Idea of protecting our resources and nature Natural places that must be protected can be grouped into different biomes. Biomes are places that have distinct climate (how much rainfall they receive and their temperatures) and types of plants and animals that thrive in these specific climates. Biomes Type of Biome Climate Desert Little rain & large daily change in temperature (hot in day & cold at night) Rainforest Lots of rain with hot temperatures Tundra Has dry & wet seasons, but very cold Grasslands Has dry & wet season. Temperature is hot. Deciduous Forest Moisture evenly distributed throughout the year. Has warm summers and cold winters. Coniferous Forest Moisture varies throughout the year. Has cool summers and cold winters. Biomes of the World Rainforest Biome Major Rainforest Desert Major Deserts Grassland Biome Major Grasslands Tundra Deciduous Forest Coniferous Forest Temperate Biomes Weather Conditions in our atmosphere such as temperature, sunshine, rain, snow and clouds. Sun is main cause for weather Certain materials heat up differently. Darker objects absorb heat from the sun better than light ones, which reflect heat better. This is why asphalt parking lots can be so hot in summer. Different surfaces heat differently, causing hot air to rise and cooler air to sink. When this happens wind occurs. Climate Amount of precipitation and the temperature an area gets throughout the year. Cleveland’s weather for today may be warm and sunny and tomorrow it could be cold & rainy. Cleveland’s climate however is warm summers, cold winters and moisture throughout the year. Why is this so?? Earth The distance around Earth's orbit is 584 million miles Earth travels in its orbit at 66,700 miles an hour, or 18.5 miles a second. Layers of the Earth Atmosphere: 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen Sediment Rocks erode, wear away, reform Metamorphic Rock- inside earth There are many cycles on and within Earth. A few of the most important are (1) atmospheric circulation, (2) ocean currents, (3) the global heat conveyor, (4) the hydrologic cycle, and (5) the rock cycle. The Rock Cycle The Water Cycle