* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aztec Empire History
Fall of Tenochtitlan wikipedia , lookup
Tepotzotlán wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
Aztec warfare wikipedia , lookup
Aztec cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Aztec religion wikipedia , lookup
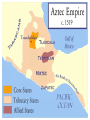
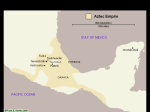
AZTEC EMPIRE 1325 CE to 1519 CE Blood, sacrifice, and the end of the world. AZTEC EMPIRE Height of influence from 1325 CE to 1519 CE Location: valley of Central Mexico Mexica (popularly known as the Aztecs) migrate into northcentral Mexico around 1325 CE Aztec Empire comprised of a number of city-states Capital city-state was Tenochtitlán (Mexico City is now on top of it) Other major city-states were Texcoco and Tlacopan (combined with Tenochtitlán, these were called the “Triple Alliance”) AZTEC EMPIRE: GOVERNMENT Basic Structure Emperor (literally, “The Great Speaker”)– ruled empire from Tenochtitlan Elected from one royal family by all of the rulers of all Aztec city-states Advised by other members of the nobility who served in various councils Each Aztec city-state ruled by a hereditary ruler Cities divided into clan-based neighborhoods called calpulli, each was ruled by a hereditary “chief” had its own local temple and school Tribute Conquered city-states were allowed to keep their own ruler and government, as long as they paid their tribute Commoners of the empire were also required to pay tribute (taxes) to the nobles of their city-state AZTEC EMPIRE: RECORD KEEPING Spoken language called Nahuatl Some basic symbols (mostly related to numbers and dates) But no fully-developed independent system of writing (most written sources are from outside, non-Aztec groups) Limited written sources BY Aztecs mean that reading about Aztecs tends to be very complicated. Watch for POV in documents about the Aztec. AZTEC EMPIRE: SOCIAL ORDER Social Classes Nobility “Speakers” = leaders of city-states of the empire Chiefs = ruled over districts within cities and served in high positions in army and government Non-noble elites Pochteca – hereditary merchant/spy class comprised of longdistance traders Artisans who made luxury items Commoners free commoners – farmers, artisans rural tenants – who lived on/worked nobles’ lands Slaves (largely prisoners of war) AZTEC EMPIRE: SUBSISTENCE Food Crops = Corn, beans, squash, amaranth, chia, tomatoes, peppers Other Crops cacao – beans used as money and to make a drink for high status people (xocolatl) cotton – for clothing Domesticated Animals = dog, turkey No beasts of burden! Hunting/fishing to supplement protein Chinampas Chinampas were man-made floating islands 17’ long x 100’ to 300’ feet wide. Aztecs built over 20,000 acres of chinampas. AZTEC EMPIRE: RELIGION Polytheistic Belief System Each calpulli had a patron god/goddess Some of the Major Deities: Huitzilopochtli – sun god Quetzalcoatl – feathered serpent and ancestor of royal family Tlaloc – rain god Human Sacrifice Mostly killing of POWs (xochiyaoyotl or “Flowery War”) Done to “feed” the sun god and maintain the world Sometimes involved ritual cannibalism Priestly Class – performed ceremonies and sacrifices Women could be priestesses Priests performed auto-sacrifice (bloodletting, scarification, etc.) Center of cities were ceremonial districts with pyramid temples and courtyard groupings AZTEC EMPIRE: COLLAPSE By about 1500, many tributary states were unhappy and planning rebellion Conquest by the Spanish in 1519 Assisted by rebellious city-states Spread of smallpox and the execution of last Emperor, Montezuma II More details on this later in Unit Four.