* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
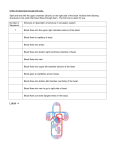
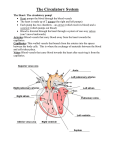
Chapter 16 Human Circulatory System Transport zInvolves the absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism Human Circulatory System z Closed circulatory system- blood is always in blood vessels. z Heart which pumps blood. z Network of blood vessels which carry blood to and from all cells of the body. Human Circulatory System (I) Three Kinds of Blood Vessels 1. Arteries 2. Veins 3. Capillaries Arteries z Thick-walled z Smooth muscle z Transports blood away from heart z Carries oxygenated blood (high levels of O2) z Arteries divide into smaller vessels known as arterioles Arteries z Thick-walled z Smooth muscle z Transports blood away from heart z Carries oxygenated blood (high levels of O2) z Arteries divide into smaller vessels known as arterioles Veins z Thin-walled z Transports blood to the heart z Carries deoxygenated blood z Contain valves which help prevent the backflow of blood z Divide into smaller vessels known as venules Capillaries z Very thin-walled (one cell thick) z Site for the exchange of materials between the blood and body tissue (cells) z Arterioles and venules are connected by capillaries Capillaries z z z Very thin-walled (one cell thick) Site for the exchange of materials between the blood and body tissue (cells) Arterioles and venules are connected by capillaries Capillaries z z z Very thin-walled (one cell thick) Site for the exchange of materials between the blood and body tissue (cells) Arterioles and venules are connected by capillaries (II) z Composed Heart of cardiac muscle z It is a 4-chambered pump composed of 2 atria and 2 ventricles z The ventricles have thicker walls than the atria z The heart pumps blood through the arteries creating a blood pressure Human Heart Human Heart Superior Vena Cava zBrings deoxygenated blood from the upper portion of the body and into the right atrium Inferior Vena Cava zBrings deoxygenated blood from the lower portion of the body and into the right atrium Right Atrium zReceives blood from the inferior and superior vena cava and pumps it into the right atrium Valves zA-V valve- separates the atrium from the ventricle zSemi-lunar valve- separates ventricles from the arteries Right Ventricle zReceives blood from the right atrium and pumps it into the pulmonary artery Pulmonary Artery zReceives blood from the right ventricle and transports it to the lungs Pulmonary Vein zReceives oxygenated blood from the lungs and transports it to the left atrium Left Atrium zReceives blood from the pulmonary vein and pumps it into the left ventricle Left Ventricle zReceives blood from the left atrium and pumps it into the aorta Aorta zMajor artery of the body zReceives blood from the left ventricle and transports it to the rest of the body Septum zSeparates the heart into a left side and a right side zLeft side contains oxygenated blood zRight side contains deoxygenated blood (III) Types of Circulation Sphygmomanometer z Instrument used to measure the pressure of the blood in the artery of the arm Ex: 120/80 120 = systolic pressure 80 = diastolic pressure (IV) Heartbeat Cycle z Diastole (relaxation)- is the period when the ventricles are filling with blood. The A-V valve is open and blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle z Systole (contraction)- is the period when the ventricle pumps blood out of the heart. A-V valve closes and the semi-lunar valve opens 1. Pulmonary Circulation zThe pathway from which blood flows from the heart Æ to the lungs Æ and back to the heart ( R.V. Æ Pulm. Artery Æ Lungs Æ Pulm. Vein Æ L.A.) 2. Systemic Circulation zThe pathway that carries blood from the heart to all parts of the body with the exception of the lungs 3. Coronary Circulation zMuscle tissue of the heart is supplied with blood through a system of coronary blood vessels zCoronary arteries- supply oxygenated blood to the muscle tissue of the heart Disorders of the Circulatory System Cardiovascular Diseases zAre diseases of the heart and blood vessels High Blood Pressure zIncreased pressure in the arteries due to stress, diet, cigarette smoking, and aging zCan lead to damage of the lining of arteries and weakening of the heart muscle Heart Attacks Two Types 1. Coronary Thrombosis 2. Angina Pectoris Coronary Thrombosis zBlockage of the coronary artery resulting in oxygen deficiency in the heart muscle Coronary Thrombosis Angina Pectoris zNarrowing of the coronary artery causing an inadequate supply of oxygen to the heart muscle