* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BLOOD TYPES : 101
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
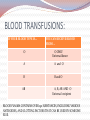
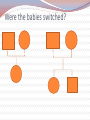
BLOOD…… Red blood cells White blood cells A LITTLE HISTORY DISCOVERED IN 1900 at the University of Vienna by Karl Landsteiner in the process of trying to learn why blood transfusions sometimes cause death and other times saved a patient. Karl won the Nobel Prize in 1930 for his discovery. Blood types Classification of blood is based on the presence or absence of inherited ( from both parents) substances (markers ) found on the surface of the red blood cells. The most familiar blood group system uses the letters A, B, O , these represent the alleles /genes that are found on chromosome 9 ( of each parent). An individual’s ABO type is determined by the inheritance of 1 of 3 alleles (A, B, O) from each parent. % BLOOD TYPES AMONG DIFFERENT populations Caucasians African American Hispanic Asian O+ 37% 47% 53% 39% O- 8% 4% 4% 1% A+ 33% 24% 29% 27% AB+ 7% 9% 2% 18% 2% 9% 0.5% 25% B- 2% 1% 1% 0.4% AB + 3% 4% 2% 7% AB - 1% 0.3% 0.2% 0.1% Blood Genotypes: phenotypes Allele from parent 1 Allele from parent 2 Genotype of offspring Blood types of offspring A A AA A A B AB AB A O AO A B A AB AB B B BB B B O BO B O O OO O CO-DOMINANT RECESSIVIE ANTIGENS An antigen is a foreign particle that enters the body. This could be a disease causing agent such as part of bacterium or virus , a particle such as pollen or dust, or foreign blood cells and cells from transplanted organs. ANTIBODIES: An antibody is a protein made by the body’s immune system. Antibodies react with specific antigens to enable the antigens to be removed from the body. FOUND IN BLOOD OR OTHER BODY FLUIDS. PRODUCED BY A TYPE OF WHITE BLOOD CELL. USED BY THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO IDENTIFY & NEUTRALIZE FOREIGN OBJECTS, VIRUSES & BACTERIA. Lock AND key fit : antigens & antibodies Rh factor Another type of marker protein on the surface of RBC. It was first identified in rhesus monkeys – that’s why it is labeled Rh. Inherited from your parents. Inherited independently of the ABO blood type alleles. Rh+ is dominant. About 85% of humans have the Rh marker. Problem: If an Rh- mother gives birth to a Rh+ infant, some fetal blood cells cross the placental barrier, and the mother receives Rh+ antigens. The Rh- mother’s immune system recognizes these antigens as foreign invaders and begins making “anti Rh” antibodies. These antibodies may then be passed on to an Rh+ fetus in a future pregnancy, causing the fetus’s red blood cells to clump, which can lead to fetal death. BLOOD TRANSFUSIONS: IF YOUR BLOOD TYPE IS…. O YOU CAN RECEIVE BLOOD FROM … O ONLY Universal donor A A and O B B and O AB A, B, AB AND O Universal recipient BLOOD PLASMA CONTAINS OVER 150 SUBSTANCES, INCLUDING VARIOUS ANTIBODIES, AND CLOTTING FACTORS THAT CAN BE USED BY SOMEONE ELSE. Blood practice problems Blood practice : co-dominance Were the babies switched?