* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychological Health
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Victor Skumin wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
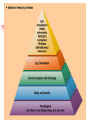
Psychological Health Chapter 3 Psychological Health Psychological health versus psychological normality What is Mentally normal? 2 3 Defining Psychological Health A negative definition A positive definition 4 5 Mental Health Abraham Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Self-Actualized Realism Acceptance Autonomy Intimacy Creativity 6 Erikson's Eight Stages of Personality Development Trust versus mistrust Autonomy versus shame and self-doubt Initiative versus guilt Industry versus inferiority Identity versus identity confusion Intimacy versus isolation Generativity versus self-absorption Integrity versus despair 7 Meeting Life’s Challenges Growing Up Psychologically Adult identity Intimacy Values and Purpose 8 Achieving Healthy Self-esteem Positive Self Concept Meeting the Challenges Less Defensive Optimism 9 Honest Communications When you are the speaker: State your concern as clearly as possible. Take responsibility for your feelings; use “I” statements. Avoid generalizations. Avoid blaming, accusing, and belittling. Ask for action ahead of time, not after the fact. As a Listener: Don’t give unsolicited advice. Listen reflectively, Don’t interrupt, judge, blame,or evaluate. Really listen, Try to tune in to the other person’s feelings. Let the other person know that you value what he or she is saying and want to understand. 10 Loneliness Balance. Unhappiness with being alone. The passive feeling. 11 Dealing With Anger Distinguish between gratuitous expression a reasonable level of selfassertiveness. Manage your anger. Dealing with anger in other people. 12 Psychological Disorders Anxiety Simple, specific phobias Social phobias Panic disorders Generalized Anxiety disorder (GAD) Obsessive-Compulsive disorders (OCD) Compulsions Post-Traumatic stress disorders (PTSD) Treatment 13 Mood Disorders Depression Signs/Symptoms Potential of suicide Helping yourself or a friend Treatment Psychotherapy Drug therapy ECT 14 Mood Disorders Suicide Risk Factors Encouragement Treatment 15 Psychological Disorders Mania Bipolar Disorder Gender differences Schizophrenia General characteristics Disorganized thoughts Inappropriate emotions Delusions Auditory hallucinations Deteriorating social and work function 16 Models of Human Nature and Therapeutic Change Four Different perspectives 1. 2. 3. 4. Biological – pharmacological therapy Behavioral – Stimulus response reinforcement Cognitive – Attitudes, behaviors and feelings Psychodynamic – thoughts Evaluation of the models 17 Getting Help Self Help Books Writing a journal Social groups Peer counseling Professional Psychiatrists Clinical psychologists Social workers Licensed Counselors Clergy Treatment Team 18