* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Offshore Finance and the Netherlands
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
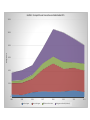
Offshore Finance, shadow banking and the issue of regulatory arbitrage Rodrigo Fernandez SOMO / KU Leuven What is shadow banking? a network of non-bank entities that intermediate credit in a unregulated market environment outside conventional banking structures. Why does it matter? • ‘Back to the future’: banking from 18th century, with 21th century technology • no public backstop • Credit creation is outside the scope of public authority • Unstable market • Complex information asymmetries • Lessons from the eurodollar markets Selected global financial indicators, Billions of Dollar, 2002-2010 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 GDP World stock market capitalization public debt securities private debt securities Bank assets OFI assets 2010 What is an Offshore Financial Center? “An OFC is a country or jurisdiction that provides financial services to nonresidents on a scale that is incommensurate with the size and the financing of its domestic economy.” IMF 2007 “An OFC may be defined as a jurisdiction in which transactions with non-residents far outweigh transactions related to the domestic economy” Bank of England 2001 Why does it matter? OFC’s enable capital to move out of the regulated environment of the nation state, which leads to: Eroding the regulatory capacity of nation states Re-scaling of finance Regulatory arbitrage Eroding the sovereignty of nation states Tax evasion Tax avoidance Top ten reporting inward FDI stock in 2011 3,500,000 Source: 3,000,000 Million of dollar 2,500,000 2,000,000 1,500,000 1,000,000 500,000 0 Size of OFI sector in the EU in 2010, in Billion of Euro 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Size of 'other intermediaries'in the Eurozone in 2010 5% 6% 27% 8% Netherlands Luxembourg France 7% Ireland Spain Italy Germany 12% Other 22% 13% Grafiek 2. Compostitie van transacties van Nederlandse BFI's 12000 10000 Miljard euro 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 2004 2005 Deelnemingen 2006 Concernleningen 2007 2008 Effecten en derivaten 2009 Leningen van derden (banken) 2010 2011 Offshore Architecture of the ‘Holland Route’ The London branch of the globally active bank acts as lead manager and arranger The Dutch SFI is a shell company and formally acts as issuer of the notes A large Dutch trust firm is responsible for all local administrative tasks and responsibilities that are related to a Dutch domicile and tax ruling Administrative functions related to the note program, are conducted by one or more banks located in the UK The notes are listed on the exchanges of Ireland, Luxembourg, or both, but are also sold OTC Conclusion • Tax avoidance and regulatory arbitrage are embedded in the same offshore industry • Difficult to disentangle financial from non financial conduit structures • Need to include problem of regulatory arbitrage in debate on tax havens Composition of the Dutch OFI sector Assets Financial SFI Credit regulatory Part of financial degree of shadow intermediation oversight/backstop corporation banking indirect Yes substantial no Yes low 500 partly Non-financial SFI 1500 no Finance company 128 yes indirect Yes substantial SPV 330 yes no Yes very high 2 yes no Yes very high 18 partly no Yes substantial MMF Hedgefund Invest. Fund 340 no no Yes low Invest. Trust 91 no no Yes medium Private equity 25 no no Yes medium 184 no no Yes low 14 no no Yes low Holding financial instit Other