* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mars Magnetic Anomalies
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
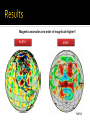
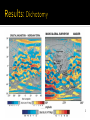
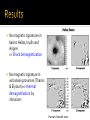
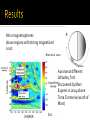
Ester Aranzana 13 de Enero de 2012 Rock core (Fe-FeS) No internal magnetic field, no dynamo action but it has one in the past mini-magnetospheres of crustal origin Mars Global Surveyor(1996) - MGS MAG: Magnetic vector data sparsely from 400-100 km - MGS ER: scalar field at 180 km Others: Balloon magnetometer Rover on Martian surface Laboratory studies Magnetic anomalies one order of magnitude higher!! EARTH MARS NASA Strong magnetization requires huge volumes (170-190 km radii, 20-30 km thicknesses) 2 faults similar to Earth faults with EW trending features alternating polarity Plate tectonics era Connerney et al. 2005 No magnetic signatures in basins Hellas, Isydis and Argyre => Shock demagnetization No magnetic signature in volcanoes provinces (Tharsis & Elysium)=> thermal demagnetization by intrusions Harkani-Hamed 2001 Mini-magnetospheres above regions with strong magnetized crust. Brain et al. 2010 Aurorae at different latitudes, first discovered by Mars Express in 2004 above Terra Cimmeria (south of Mars) ESA - Cessation of the core field around 4.1 Gyr By cooling of the planet. - Origin dichotomy: the new mode is a huge impact Other explanations: Volcanic features, plate tectonics - Faults, lineations => Plate tectonics era in presence of a reversing dynamo - Internal magnetic field in the past =>The evolution of climate and habitability in Mars Roberts et al. 2009 Connerney, J.E.P, Acuña, M.H. et al. 2005, Tectonic implications of Mars crustal magnetism, PNAS October 18, 2005 vol. 102 no. 42 14970-14975. Roberts, J.H., Lillis, R.J., Manga, M. 2009, Giant impacts an Mars cessation of the Martian dynamo, JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114, E04009, doi:10.1029/2008JE003287, 2009 Jafar Arkani-Hamed 2001, A 50-degree spherical model of the magnetic field of Mars, JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO.10, PAGES 23,197-23,208. Purucker, M., Ravat, D., Frey, H., Voorhies, C., Sabaka, T. & Acuña, M. 2000, An altitude-normalized magnetic map of Mars and its interpretation, GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 27, NO. 16, PAGES 2449-2452. Acuña, M. H., Connerney, J.E.P et al. 2001, Magnetic field of Mars: Summary of results from the aerobraking and mapping orbits, JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. E10, PAGES 23,403–23,417 Brain, D.A., Baker, A.H., Briggs, J., Eastwood, J.P., Halekas, J.S. & Phan, T.D. 2010, Episodic detachment of Martian crustal magnetic fields leading to bulk atmospheric plasma to escape, GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.37, L14108. Planetary Sciences, Imke de Pater & Jack J. Lissauer, Cambridge University Press 2001.