* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8: Electronic Circuit Design and Construction
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
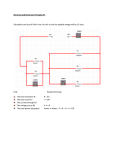
Assignment title DC Networks Assessor Paul Lewis Date issued Final deadline Duration (approx) 2 sessions (8 hours) Qualification suite covered BTEC Extended Diploma in Engineering Level 3 Units covered A part of Unit 6 Electrical and Electronic Principles Learning aims covered Be able to use circuit theory to determine the current, voltage and resistance in direct current (DC) circuits Scenario You have been employed as a junior technician in a local electronics company who make power supplies. A new power supply has appeared on the market which used considerably less power that the one made by your company. You have been commisioned by your managing director to investigate the power drawn by your power supply circuits and suggest possible alternatives Task 1 Part a) For the circuit shown below: Choose 5 different value resistors from the following table for resistors R1 – R5 Calculate the total power dissipation of your circuit then choose a suitable voltage from the table below based on this value Resistor values for R1 – Voltage values for V1 R5 10 Ω 3 volts 22 Ω 5 volts 33 Ω 6 volts 47 Ω 9 volts 100 Ω 10 volts 220 Ω 12 volts 330 Ω 15 volts 470 Ω 24 volts 1k Ω © Pearson 2014 1 Calculate: The total circuit resistance Rt The total circuit current It The current flowing through R3 The voltage dropped across R2 The power dissipated by R1 Confirm the results of your calculation using the laboratory simulator (Multisim) Care should be taken by each student to ensure that where possible, the combination of components and supply voltage are unique for each assessment. Part b) Check your calculations for P1 by constructing the circuit on breadboard and carefully measuring the values of resistance, current and voltage as specified. Make a table similar to the one shown below and enter your values. Parameter Calculated values Measured values Simulated values Total circuit resistance Total circuit current Current flowing through R3 Voltage dropped across R2 Power dissipated in R1 Part c) Use DC circuit measurements to calculate the internal resistance of a battery Measure the offload voltage of a given battery using a multimeter Measure the onload voltage of the battery when connected to the virtual cat circuit using a multimeter Measure the current drawn by the virtual cat circuit using a multimeter Use the data from the measurements to calculate the internal resistance of the battery Include all of the above data in a technical report © Pearson 2014 2 Part d) You are required to use test equipment to measure the forward and reverse characteristics of two semi-conductor diodes. You should use a 1N4001 diode and a zener diode to carry out this experiment. Use the following circuit as a basis for this test: Draw and label a diagram of the 1N4001 general purpose diode connected in forward bias and reverse bias mode Measure the forward characteristic of the diode between 0.5 volts and 0.7 volts using steps of 0.01 of a volt by adjusting the resistance box R1 Measure and record the reverse characteristic of the diode using Multisim between 49.9 volts and 50.01 volts using steps of 0.01 of a volt Carry out a similar experiment on a zener diode (of your choice) using its data sheet as a guide to the magnitude of voltages required to test its forward and reverse characteristics Draw and label graphs of both data sets Compare the two graphs showing the conduction characteristics of both diodes, consult the data sheets and evaluate your findings in terms of forward and reverse voltages, power dissipation and maximum operating current Evidence you must produce for this task Formulae, calculations and solutions neatly presented Photographic evidence showing the DC Network for both resistors, diodes and the internal resistance of a battery. Photographic evidence of all readings taken by the multimeter Readings taken for the forward and reverse current and voltages through and across both diodes to be neatly tabulated Graphs to be drawn to show the conduction characteristic of both diodes in both forward and reverse bias modes Your evidence should be presented in the form of a report which contains and introduction to each task and a written conclusion Criteria covered by Task 1: Unit Criterion reference Use DC circuit theory to calculate current, voltage and resistance in DC Networks Use a multi-meter to carry out circuit measurements in a DC circuit 6 P1 6 P2 Compare the forward and reverse characteristics of two different semi-conductor diodes 6 P3 To achieve the criteria you must show that you are able to: © Pearson 2014 3 Task 2 For the circuit shown below: Use the same table as for Unit 6 P1 in order to choose component values. Circuit 2 From the attached table choose different values for R1 – R3 From the attached table choose different voltages for V1 –V2 Use Kirchoff’s laws to determine the current flowing through R1, R2 and R3 Determine the power dissipation in R1 Use Multisim to confirm the results of your calculations and attach to the assignment as a screen dump Evidence you must produce for this task Formulae, calculations and solutions neatly presented A screen dump from a simulation showing the current through R1 and the voltage across R1. Criteria covered by Task 2: To achieve the criteria you must show that you are able to: Use Kirchoff’s laws to determine the current in various parts of a network having four nodes and the power dissipated in a load resistor containing two voltages sources Task 3 Unit Criterion reference 6 M1 The circuit shown below is a simple voltage regulated power supply: Investigate the function and operation of the circuit and choose components to produce an output voltage with the following specification: Output voltage = 5 volts © Pearson 2014 4 Output current up to a maximum of 100 mA Ripple voltage <10mV The values can have a tolerance of +/- 5% Simulate the circuit to prove its operation Evidence you must produce for this task Explain how and why the value for each component was chosen Build and test the final solution and evaluate its performance against the given specification Formulae, calculations and solutions neatly presented Photographic or video evidence of the circuit with readings showing that the circuit is performing to specification A simulation proving that the components chosen allow the circuit to perform within the specified parameters Criteria covered by Task 2: To achieve the criteria you must show that you are able to: Analyse the operation and the effects of varying component parameters of a power supply circuit that includes a transformer, diodes and capacitors Unit Criterion reference 6 D1 Sources of information Websites http://www.bassix.eu © Pearson 2014 5