* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxygen Transport System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
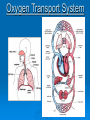
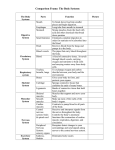
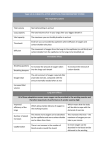
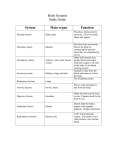
Oxygen Transport System What is the Oxygen Transport System? The Oxygen Transport System is made up of the system and the system. The aim of the Oxygen Transport System is to provide our working muscles and organs with energy, which we get from the oxygen we inhale. What is Respiration? Respiration is the process where we breath in Oxygen and then release Carbon Dioxide. • Inhaling – taking in Oxygen (O2) • Exhaling – releasing Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Oxygen is breathed in through the nose and mouth. This Oxygen travels to our lungs. The Oxygen is then transported around the body in our Blood (OXYGENATED BLOOD). Muscles and our vital organs use this oxygen for energy. Our blood then transports a waste product called Carbon Dioxide back to our lungs (DEOXYGENATED BLOOD) This Carbon Dioxide is then released through our nose and mouth. Circulatory System This system involves the heart, blood and blood vessels. It is the process where blood is pumped around the body supplying working muscles and organs with oxygen. Pulmonary Circulation – takes the blood from the heart to the lungs, and then back to the heart. Systemic Circulation – takes blood from the heart, around the body and then back to the heart. The blood leaves the left side of the heart and is pumped around and returns to the right side. Arteries carry the blood away from the heart Veins carry the blood back to the heart This system carries on from the work of the respiratory system – transports the oxygen taken into the lungs. To enable us to exercise, our body must continuously deliver to our working muscles and organs. The process where we inhale and exhale air is called . We breath in into our Blood then absorbs the oxygen, becoming . blood. Our pumps this blood around our bloody, providing our muscles and organs with oxygen. The blood then becomes due to using up the oxygen and collecting the waste product of respiration, called . This is then taken back to the via the heart, and is exhaled back into the air. The system where our blood is continuously pumped around our body is called the system. The components which make up this system are the blood , and our blood. , There are two parts of this circulation: 1) Pulmonary Circulation where the blood travels from the to the and back to the heart. 2) Circulation, where the blood travels from the heart, around the lower and upper body then back to the heart. Oxygenated blood leaves from the is carried round the body by side of the heart, and . De-oxygenated blood is carried back to the heart by enters the side. and The heart continuously repeats this process by pumping blood around the body so our muscles and organs receive and dispose of . What is happening to our body when exercising? When we exercise we: - Increase our Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - Increase body temperature - Increase rate of breathing - Produce sweat - Produce Carbon Dioxide and Lactic Acid Waste Products of Exercise When we exercise we are constantly breathing out: CARBON DIOXIDE If you are working at short duration / high intensity exercise (ANAEROBIC) then the oxygen you take in isn’t enough. This then results in the build up of LACTIC ACID Improving our Oxygen Transport System? We can improve our Oxygen Transport System through completing a regular training programme With an improved Oxygen Transport System: - we become more able to cope with exercise - size of heart increases (chambers of heart become thicker and stronger) - resting heart rate is slower - lung capacity increases (we can breath in more air at higher speed) - we can cope with more lactic acid during exercise As we get fitter we find exercise easier to perform. Therefore we don’t need to put as much effort in to do the same amount of work. What is Oxygen Debt? Oxygen debt is when there is a lack of Oxygen in the body for the exercise you are completing. As a result LACTIC ACID builds up in the muscles. At the end of exercise we take in extra Oxygen. This extra oxygen allows us to: - remove LACTIC ACID - replace oxygen stores in our bodies Improving Your Cardio-Respiratory Endurance Aerobic Exercise - steady pace - longer duration - muscles demand a steady supply of Oxygen - heart and lungs can cope with the demand for Oxygen Anaerobic Exercise - Short, fast bursts - muscles demand lots of Oxygen over short a period of time - heart and lungs can’t cope with the demand for Oxygen - Lactic Acid builds up quickly due to not enough Oxygen REVISION QUESTIONS The respiratory system involves the inhaling of oxygen and exhaling or carbon dioxide