* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geology and Layers of the Earth notes
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
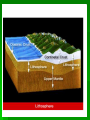
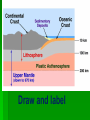
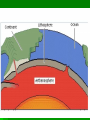
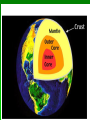
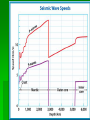
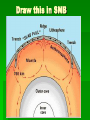
Date: Geologist & Entry: Earth’s Interior 1. Geology: study of Earth and processes that shape Earth. A. Geologist = scientist that study Earth I. Constructive forces a. building up mountains and landmasses i. earthquakes ii. volcanoes II. Destructive forces a. slowly wear away i. erosion 2. Basic Structure of Earth A. crust The outermost layer I. Thinnest - oceanic crust Thickest - continental crust II. Lower Crust is also called the lithosphere Draw and label III. Oceanic crust is basalt and is more dense than continental crust of granite B. mantle is the largest layer I. Top portion is called the asthenosphere II. Density increases with depth due to increasing pressure III.Hot softened rock mostly iron and magnesium C. outer core is beneath the mantle I. It is a slow flowing liquid of iron and nickel II. Density, temperature and pressure increase III. Spinning of liquid creates magnetic field D. inner core Earth’s center is solid, made mostly of iron and nickel I. Heaviest material and most dense layer II.Hottest layer 3. A review wave movement Density of material = speed change More dense faster, less dense slower Density change = direction change Greater the difference in density the greater the direction changes 4. Mapping Earth’s Internal Structure (How we know) I. seismic waves change as they travel through materials with different densities II. densities increase with depth as pressures increase so waves travel differently III. Use seismic waves used to map Earth’s internal structure 5. Layer Boundaries A. Seismic waves travel faster through a more dense solid region, Slower in the less dense liquid region Solid = faster Liquid = slower More dense=faster Less dense=slower C. Seismic waves speed up when they pass from the crust into the mantle I. Mantle is more dense D. Outer core is liquid because secondary seismic waves do not go through liquid E. Primary waves slow down at liquid outer core, speed up at solid inner core Draw this in SNB click here to watch video of Earth's layers