* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
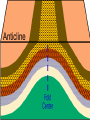
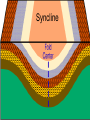
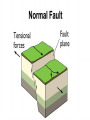
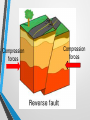
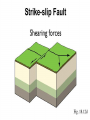
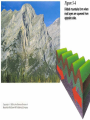
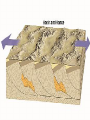
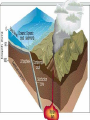
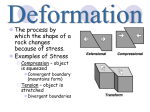
What to do… •Answer these 2 questions in your journal! •1. Tectonic plates consist of… a. continental crust. b. oceanic crust. c. both continental and oceanic crust. d. mesosphere. •2. The deep interior of the Earth can be mapped using a. seismic waves. b. sonar. c. information from drilling expeditions. d. ocean waves. Deforming the Earth’s Crust Standards: Chapter 15, Section 4 7.5 – Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year 7.6 – Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading Deformation •Stress is the amount of force per unit area on a given material •The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called deformation • Two types of deformation can occur to rocks under stress • Layers can bend when stress is applied to them • When too much stress is applied, they can reach their elastic limit and break Compression & Tension • Compression is the type of stress that occurs when an object is squeezed • Tension is stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object Folding •Folding is the bending of rock layers because of stress in the Earth’s crust •By assuming all rock starts in horizontal layers, scientists know deformation has occurred when they see a fold. Types of Folds • Anticlines, upward, arching fold • Synclines, downward, trough-like folds • Monoclines, horizontal Anticline Syncline Faulting • Some rock layers break when too much stress is applied to them. • The surface along which a rock breaks and slide past each other is called a fault • The two sides of a fault are known as the hanging wall and the footwall • The type of fault that forms is dependent on where the hanging and footwall are located Types of Faulting •There are three types of faults that occur •Normal Faults •Reverse Faults •Strike-Slip Faults Normal Faults •When rocks are pulled apart because of tension, normal faults often form •When a normal fault moves, it causes the hanging wall to move down relative to the footwall Reverse Fault • When rocks are pushed together by compression, reverse faults often form • When a reverse fault moves, it causes the hanging wall to move up relative to the footwall Compression forces Compression forces Strike-Slip Fault •Forms when opposing forces cause rock to break and move horizontally Plate Tectonics & Mountain Building • When tectonic plates collide, land features that start as folds and faults, can eventually become large mountain ranges Folded Mountains • Form when rock layers are squeezed together and pushed upward • These mountains form at convergent plate boundaries • Appalachian Mountains 390 million years ago Fault-Block Mountains • Fault-Block mountains form when tension causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks • Often leaves sharp, jagged peaks Volcanic Mountains • Located at convergent plate boundaries where oceanic crust sinks into the asthenosphere at subduction zones • The rock that is melted at subduction zones forms magma which rises to the surface and erupts • Sometimes these mountains can rise above the sea and become islands • A majority of the tectonically active volcanic mountains have formed around the Pacific Plate which is known as the Ring of Fire Uplift and Subsidence •Uplift is the rising of regions of Earth’s crust to higher elevations •Subsidence is known as the sinking of Earth’s crust to lower regions Uplifting of Depressed Rock • One way areas rise without deforming is a process known as rebound • Rebound occurs when the crust slowly springs back to its previous elevation • Rebound happens when a weight is removed from a region ( glacial melting) Tectonic Letdown • Subsidence can occur when the lithosphere becomes stretched • A rift zone is a set of deep cracks that forms at a divergent plate boundary • As the plates move apart, the rift zone begins to subside between the plates Put it together… •Complete your study guide! •It is due tomorrow!