* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing concepts
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
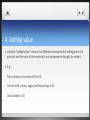
Important Marketing Concepts 1. Segmentation A market segment is a sub group of a whole market in which consumers have similar characteristics. Identifying these groups and marketing different products to them is segmentation. Companies try to produce different products to different segments to maximise sales. E.g. soft drinks market. Segementation can be through; Geographic differences Demographic differences Psychographic differences (lifestyles/personality) 2. Mass marketing and niche marketing Niche marketing involves identifying and exploiting a small part of a larger market. Mass marketing is the exact opposite. It involves selling the same products to the whole market with no attempt to target groups within it. (Coca-Cola) Advantages of niche marketing Small firms able to survive and thrive If the market is unexploited, opportunity to sell at high prices and high profit margins until competition enters the market. Niche market products can also be used by large firms to create status and image. Advantages of mass marketing Small niches do not allow for economies of scale. Mass market has lower average costs. Mass market strategies run less risks than niche strategies. Consumer trends/fashions can lead to business failure if they concentrate on one niche market. 3. Market share, market size and market growth Successful marketing requires firms to understand Which market they are operating in Who their consumers are Whether the market is growing or shrinking And what their share of the market is. A market means “who the consumers are” no longer a place where buyers and sellers meet. The market is potential customers. To calculate market share: Sales of the business x 100 Total market sales High market share is beneficial as: Higher sales than competitors Retailers keen to stock and promote best products Market leader can influence the whole market. Market growth is measure by the percentage increase in the size of the whole market. Firms must be careful when analysing market growth, as the whole market might grow while a segment might be shrinking or vice versa. Identifying the markets with the highest growth potential is one of the keys to success of business organisations. 4. Adding value Literally, “added value” means the difference between the selling price of a product and the cost of the materials and components bought to make it. E.g. Tub of luxury ice cream sell for $4 Cost of milk, cream, sugar and flavourings is $1 Value added = $3 This is not the same a profit as it does not include wages, rent and other costs. If a business is able to increase added value then the potential for greater profits is clear. Strategies to “add value” Create exclusive/luxurious image High quality packaging to differentiate the product from competitors (used in cosmetics and confectionary) Promote brand so it becomes a “must have” which consumers will pay a premium price for. Create a USP (unique selling point)