* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
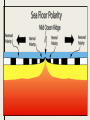
What to do… ■ Answer the following questions in your journal 1. Which of the following lists the Earth’s layers in order from hottest to coldest in temperature? a. Outer core, mantle, inner core, crust b. Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core c. Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust d. Mantle, crust, inner core, outer core 2. Which of the following components would you least likely to find in the Earth’s mantle? a. Iron b. Aluminum c. Nickel d. Silicon 3. Which of Earth’s layers is the thinnest? a. Crust b. Mantle c. Inner core d. Outer core Answers: 1. Which of the following lists the Earth’s layers in order from hottest to coldest in temperature? a. Outer core, mantle, inner core, crust b. Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core c. Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust d. Mantle, crust, inner core, outer core 2. Which of the following components would you least likely to find in the Earth’s mantle? a. Iron b. Aluminum c. Nickel d. Silicon 3. Which of Earth’s layers is the thinnest? a. Crust b. Mantle c. Inner core d. Outer core Restless Continents State Standard: 7.6 – Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading Think about it? • Alfred Wegener hypothesized that all of the continents were once one large landmass (Pangaea) that has broken up and drifted apart. Evidence • Continents fit like pieces of a puzzle • Fossils of same species of animal & plants found on separate continents • Matching mountain chains • Coal fields in Antarctica • Rock formations • Climatic conditions • Pangaea – Greek for “ all Earth” • Pangaea broke into two huge continents – Laurasia – Gondwana • These two split again to form the current continents Mid-Ocean Ridges and Sea Floor Spreading • Mid-ocean Ridges – Underwater mountain chain that runs through the Earth’s oceans. • Sea-floor spreading – Process in which new lithosphere forms • Magma rises to the surface through the mid-ocean ridge forming new oceanic crust • Tectonic plates spread apart and magma fills the gap. • As new crust forms older crust moves away from the M.O.R. • Earth’s north and south poles have changed places many times • Molten rock contains contains tiny grains of magnetic minerals • These minerals align with the magnetic field of the Earth. • As the magnetic field reverses and the ocean and new ocean floor is formed it leaves a record of this change. Sea Floor Spreading Put it together! ■ Begin working on your study guide. ■ Study guides due on Thursday!