* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functions of the eye parts
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
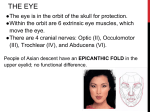
Functions of Eye Parts Aqueous Humor - Between the iris and the cornea is a space filled with a watery fluid called the aqueous humor. This has a refractive index of 1.336. The aqueous humor bathes both the cornea and the lens. Cornea - The front portion of the sclera has a section that is transparent. This transparent window known as the cornea is attached to the sclera and is a major refractive power of the eye. The refractive index is 1.376. The cornea acts as the eye's outermost lens. It functions like a window that controls and focuses the entry of light into the eye. Iris - The iris is a muscular and pigmented tissue forming a circular curtain with a hole in the centre. The hole in the centre of the iris is called the pupil. The iris controls the amount of light which enters the eye by changing the pupil's diameter. Optic Nerve The optic nerve connects the retina to the lateral geniculate nucleus, which is in the middle of the brain. This is the first connection made by the visual system in the brain. Retina - The retina is made up of transparent, sensory and nervous tissue carrying blood vessels, nerve cells and nerve fibers. At the back of the retina, the nerve fibers all come together and emerge as the optic nerve. The nerve endings on the inside of the wall of the retina terminate in light-sensitive cells of two types, rods and cones. Rods are used for peripheral vision and night vision. Cones require bright light and provide fine detail and color vision. The point on the retina where the nerve fibers leave to form the optic nerve is called the optic disc or blind spot. Sclera - The outside covering of the eye is a protective envelope of leathery connective tissue known as the sclera. This is the white coating on the outside of the eyeball, commonly known as the white of the eye. It completely envelops the globe except at the front of the eye and maintains the shape of the globe. It also provides a firm anchorage for the extra ocular muscles that control the eye's movement. Lens - provides a clear medium through which light rays from an object can reach the retina focuses a sharp image of an object on the retina varies its refractive power, thus providing clear images of objects over a wide range of distances flatter = longer focal length and vision for distance rounder = shorter focal length and vision for close up creates a functional barrier between the anterior and posterior segments of the eye the refractive index of the lens is 1.376 – 1.406 Tapetum - A reflective layer under the retina which serves to intensify vision in dim light. The "mirror" effect of the tapetum results in the "eye shine" observed when an animal looks into a car's headlights. While dim light vision is enhanced by the tapetum, scattering of the reflected light may result in reduced acuity. Vitreous Humor - A jelly-like transparent fluid fills the inner chamber of the eye. This fluid is called the vitreous humor, and it is contained in a thin membranous sac called the hyaloid membrane. The fluid of the vitreous humor has a refractive index of 1.337. Note For you to see clearly, light rays must be focused by the cornea and lens to fall precisely on the retina. The retina converts the light rays into impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain, which interprets them as images.