* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Igneous Rock
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Ore genesis wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
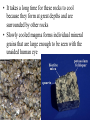
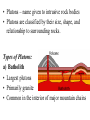
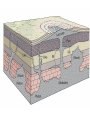
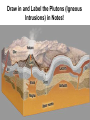
Igneous Rock • Igneous means “born of fire”. • Formed when magma or lava cools and hardens through the process of crystallization • Crystallization = the formation of mineral grains • Classified by texture (cooling rate) and composition (color) • Usually made of 2 or more minerals • Contains no fossils • Has no layering • Rarely reacts with acids • Can be light-colored to dark-colored • Can be fine-grained, coarse-grained, or glassy • Resistant to weathering Two Types of Igneous Rock: 1) Plutonic Igneous Rock (intrusive) 2) Volcanic Igneous Rock (extrusive) • Formed from magma within Earth • Magma is melted rock material composed of common elements and fluids • As magma cools, atoms and compounds in the liquid rearrange themselves into new crystals called mineral grains • Rocks form as these mineral grains grow together • Rocks that form from magma below the surface are called intrusive igneous rocks (PLUTONS) • It takes a long time for these rocks to cool because they form at great depths and are surrounded by other rocks • Slowly cooled magma forms individual mineral grains that are large enough to be seen with the unaided human eye • Plutons – name given to intrusive rock bodies • Plutons are classified by their size, shape, and relationship to surrounding rocks. Types of Plutons: a) Batholith • Largest plutons • Primarily granite • Common in the interior of major mountain chains b) Stocks • Massive pluton that formed from a magma chamber • About the size of a mountain c) Laccolith • A mushroom-shaped pluton with a round top and flat bottom • Occurs as a result of intense heat and pressure d) Sill • Forms when magma intrudes into parallel layers of rock • Few centimeters – hundreds of meters in thickness e) Dike • Pluton that cuts across pre-existing rock Draw in and Label the Plutons (Igneous Intrusions) in Notes! • Formed from lava at the surface • When lava cools at the surface, it is exposed to air and water and cools quickly • Quick cooling prevents mineral grains from growing large • Used as building materials • Interlocking mineral grains make igneous rocks strong • The minerals that they are made up of are more resistant to weathering • Ores – a metal-bearing mineral or rock that can be mined for a profit • Ores are often associated with igneous intrusions (magma that cools into rock inside Earth). • Fluid left during magma crystallization contain high levels of silica, water, and any leftover elements that were not included into the common igneous minerals (gold, lead, silver, copper). • These elements along with the dissolved silica are released at the end of magma crystallization in a hot, mineral-rich fluid that fills cracks and voids in the surrounding rock.