* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intravascular Dosing, Clearance, and Volume of Distribution
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
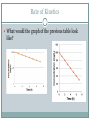
Introduction to Drug Disposition, Clearance, Volume of Distribution, and Intravascular Dosing ALLIE PUNKE PHARMACOKINETICS TUTORING FALL 2016 This is only to be used as a guide I am not involved in the selection of test questions. This is not to replace studying for the exam; only to supplement study. Just because it is discussed today does NOT mean it will be on the test. Just because it is omitted in this review does NOT mean it will be omitted from the exam. Tips for Pharmacokinetics Learn the formulas! Know to go back and forth between each of them depending on the type of information you were given. Study especially hard for the first few exams…since the material will build on itself Make sure to always look at the units Introduction to Drug Disposition Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacogenetics: Pharmacogenomics: Pharmacometrics: ADME Absorption: What are the two types? Distribution: Acidic drugs bind to ___________, while basic drugs bind to _________________ True or False: A drug that has a high Volume of distribution (Vd) means that it is very hydrophilic. ADME Metabolism: Which of the following is an example of a Phase II reaction? A. Hydrolysis B. Methylation C. Reduction D. Oxidation E. A and B What is the overall goal of liver metabolism? Intestinal metabolism affects _________, while liver metabolism affects ______________. Elimination: Liver or kidney Rate of Kinetics True or False: Zero-Order kinetics removes a constant fraction of drug Zero Order Dependent on concentration? Constant amount or fraction removed? First Order Rate of Kinetics Is this data an example of zero or first order? Time (h) Concentration 0 215 2 182 4 149 6 116 8 83 10 50 Rate of Kinetics What would the graph of the previous table look like? Clearance Clearance: The theoretical volume of blood from which drug is irreversibly removed per unit time Equations for Clearance: CL= CL= A patient is given 500 mg of a new drug. Plasma concentration entering the liver was 360 mg/L, and the concentration exiting the liver was 95 mg/L. (Assume liver blood flow is 81 L/h). What is the ER of the drug? Is it a high or low extraction drug? What is the CL of the drug? Clearance A patient is given 750 mg of a new drug. Plasma concentration entering the liver was 165 ng/L. The extraction ratio is 35%. What is the concentration leaving the liver? Clearance A patient is given 300 mg of a drug that has Vd of 75 L. Hepatic CL=900 ml/h, which is 60% of total CL. What is the total CL? How much is renal CL, if it is 10% of hepatic clearance? What is the half-life of the drug? Basics of CL and Vd True or False: If CL is increased, then Vd is also increased. How many half lives does it take to reach steady state? Calculating time to steady state: If k=0.0144 h-1, then ____ hours to reach steady state Css occurs when _________ is equal to ________ Css equation= Intravascular Dosing What is the initial concentration if 1000 mg of drug (Vd=0.7 L/kg) is given to a patient (90 kg) via IV bolus? When would you expect to see the maximum/peak concentration? Intravascular Dosing Time (hr) Concentration 2 1.07 mcg/mL 10 0.342 mcg/mL Calculate the elimination rate constant and the halflife of the drug. Intravascular Dosing A drug is given to a patient and at hour 2 and 9, the concentrations are 70 mg/L and 40 mg/L. What is the half-life? What is the initial concentration and concentration at hour 7.5. How long will it take (starting from the time the drug was given) for the drug concentration to reach 2.5 mg/L? Intravascular Dosing What is the Vd (assume the dose was 2 grams)? What is the CL? What is the AUC? Intravascular Dosing After an IV Bolus of 100mg of a drug, what is the area under the curve? What are the correct units for AUC? Given k = 0.186 h-1 and Co = 6.0 mg/L Questions? [email protected] ENJOY YOUR WEEKEND!