* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Church and The Crusades - Spectrum Loves Social Studies
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
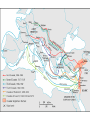
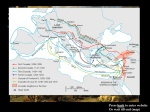
The Church and The Crusades Bellwork • Review: • In your own words, explain how the Catholic church came to have so much power over the people in the Middle Ages: • In your own words, explain how the Catholic church came to be so rich in the Middle Ages: Cathedrals • Some of the money that the church brought in was invested in grand buildings for worship • For most towns, this was the main gathering spot for all of life’s occasions– baptisms, marriages, and burials– as well as for the sacred objects of a town, such as the possessions or remains of saints • The architectural style known as Gothic included buttresses as support the tall structures The World in 1050 (from Prentiss Hall World History) • In 1050, as Western Europe was just emerging from a period of isolation, many other civilizations were thriving elsewhere. The religion of Islam had given rise to a brilliant civilization that stretched from presentday Spain to India, and Muslim traders and scholars spread goods and ideas even further. • India was a land of thriving cities where Hindu and Buddhist traditions flourished and wealthy princes built stunning temples and palaces. In East Asia, under the Tang and Song dynasties, China’s culture flourished and influenced neighboring peoples. Meanwhile, the Soninke people of West Africa were building the great trading empire of Ghana. • Across the Atlantic, in Central America, the Maya had cleared rain forests and built cities with towering temples. In the Andes of South America, Native Americans were building a great empire. The civilizations of the Americas, however, remained apart from the contacts that were taking place among Africans, Europeans, and Asians. • Closer to Western Europe, the Byzantine empire- the former eastern Roman Empire- was generally prosperous and united. In the 1050s, the Seljuk Turks invaded. . . [and] extended their power over the Holy Land, that is, Jerusalem and other places in Palestine where Christians believe Jesus lived and preached. . . The conflict prevented Christian pilgrims from traveling to the Holy Land. The Call to Crusade • The Pope called on Christian knights to help recapture the Holy Land (and make it safe for pilgrimages) • Thousands responded by heading off to fight in 1096, but few returned • Reasons for crusading: – True religious motivations – Hoping to win wealth, land, or adventure – Hoping to escape troubles at home The Crusades • There were many “waves” of actual crusades of a period of about 200 years • The first crusade succeeded in its goal of recapturing Jerusalem – Crusaders massacred Muslim and Jewish residents of the city when they arrived (this pattern repeated as they took other cities) – There were more Muslim land holdings, though, so the work was not done • Later crusades occurred throughout the Middle East and North Africa – At times, Christians fought non-Muslims • Looted and massacred Christians in the Christian capital of Constantinople • 20,000 Cathars in France were mutilated and massacred • Frequent attacks and massacres in Jewish towns – Both Muslims and Christians committed atrocities during the Crusades • By the end, the Holy Land was recaptured by the Muslim leader Saladin. The Reconquista/The Inquisition • Spain (which had been conquered by Muslim invaders in the 700s) was also a focus of crusaders • Eventually, Christian forces had re-conquered Spain (reconquista) and were in control but Muslim influences remained strong • In the late 1400s, the King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain, along with the Church, began the Inquisition: a court set up to try people accused of not being Christian – Tried Muslims and Jews, mostly – If found guilty, they often were burned at the stake – Was used against people for not being the RIGHT kind of Christian, too…anyone could accuse you – 150,000 people fled Spain to escape the Inquisition The Effects of the Crusades • Europe expanded its trade with the rest of the world, which helped its economy • Europe expanded its worldview; for the first time since the Roman Empire fell, it had contact with new cultures and ideas! • New taxes were put into place to help pay for the crusades • Various popes and kings throughout this period gained greater power and prestige • Left a legacy of hatred, distrust, and resentment between Christians, Muslims, and Jews Your Job: • You have gone on crusade! • Write a letter home telling your family about what you have seen, what you have done, and how you feel • You get to decide your age, location, motivations, and current feelings