* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download In a series circuit
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
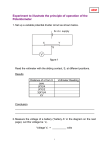
‘Current and voltage in series circuits’ L/O :- To understand how current and voltage behave in a series circuit ‘Current and voltage in series circuits’ L/O :- To understand how current and voltage behave in a series circuit Starter in back of books: True or false: 1. Static electricity is the build of protons on an insulating material. 2. Like charges repel e.g. 2 negative electrons push each other apart. 3. Static builds up when two conductors are rubbed against each other. 4. Friction between any two insulating materials causes static electricity. 5. Lightening happens when hot air rubs against cold air causing a build up of static electricity. Quick quiz- back of your books: • Name 2 things that can affect thinking distance when stopping a car • Name 2 things that can affect braking distance when stopping a car • What 2 things does your momentum depend on? What can you say about these circuits How can we remember the 2 types of circuit? SERIES or PARALLEL Hint: How do the episodes of a T.V. series go? Each component comes one after another in a series. Episode 1 then Episode 2 then episode 3 (never episode 1 at the same time as 2!) 1 then 2 in series Hint: What does parallel mean? Branches of a circuit are parallel to each other Remember: the voltmeters have to measure the voltage across the component, whereas the ammeter has to measure the current between components 1 2 A2 v2 Information to write down 1. Voltage across cell 2. Voltage across bulb 1 3. Voltage across bulb 2 4. Current between cell and bulb 1 5. Current between bulb 1 and bulb 2 6. Current between Bulb 2 and cell TASK Look at the statements below. Your task is to find out which of these is correct and to provide evidence to support your answer a) b) c) d) Current in a series circuit remains the same Current in a series circuit is used up as it travels through the components Voltage is shared between the components in a series circuit The voltage from the bulb is the same throughout a series circuit Assessment - You will be assessed on the evidence you provide for your answer. You should create a table and use the data to back up which statements you think are true Remember: the voltmeters have to measure the voltage across the component, whereas the ammeter has to measure the current between components 1 2 A v Information to write down 1. Voltage across cell 2. Voltage across bulb 1 3. Voltage across bulb 2 4. Current between cell and bulb 1 5. Current between bulb 1 and bulb 2 6. Current between Bulb 2 and cell Notes to take: In a series circuit: Voltage is shared between components. Current is the same around each point of the circuit. For example: If a cell provides 10V and there are 2 identical bulbs in series, then the voltage across each bulb would be 5V. If the same cell provides a current of 3Amps, then the current through each bulb will be 3 Amps. Your evidence . . . • Is your evidence repeatable? How do you know? • Is your evidence reproducible? How do you know • Is your data accurate? How do you know? • Is your data precise? How do you know? Accurate Precise Close to the true value Close to the MEAN value Using your rules, what would you expect to happen to these components as the resistor was changed a) ammeter b) Voltmeter c) A bulb What have you learnt? • Do you know the rules for current in a circuit series • Do you know the rules for voltage in a circuit series? • Can you explain why this happens • Can you explain the difference between repeatability and reproducibility? • Can you explain the difference between accurate and precise data