* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Nutrition - California Science Teacher
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Base-cation saturation ratio wikipedia , lookup
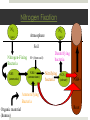
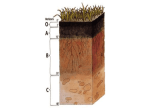
Plant Nutrition Powerpoint adopted from: http://209.85.173.132/search?q=cache:MhSZ0kbKXowJ:teachers.sduhsd.net/lolson/AP%2520Biology/ Powerpoint%2520files/35Ch37PlantNutrition2005a.pdf+ap+biology+plant+nutrition&hl=en&ct=clnk&c d=2&gl=us&lr=lang_en&client=safari http://www.holmdel.k12.nj.us/faculty/cconover-pannone/Plants/Plant%20Nutrition.pdf Nutritional Needs Autotrophic does not mean autonomous Plants need… Sun as an energy source Inorganic compounds as raw materials Water (H2O) CO2 minerals Essential Elements Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) Carbon (C) Oxygen (O) Hydrogen (H) Nitrogen (N) Phosphorous (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium (Ca) Magnesium (Mg) Micronutrients (needed in very small amounts) Chlorine Iron Manganese Boron Zinc Copper Nickel Molybdenum Nutrient Deficiency Lack of essential nutrients Exhibit specific symptoms Dependent on function of nutrient Dependent on solubility of nutrient Water and mineral uptake Water uptake Cation uptake Plants cannot extract all water from soil, only free water Cation uptake is aided by H+ secreation by root cells (proton pump) osmosis Active transport The Role of Soils Plants are dependent on soil quality Texture/structure Relative amounts of various sizes of soil particles Composition Organic and inorganic chemical component Fertility Importance of organic matter Topsoil Most important to plant growth Rich in organic matter Humus Decomposing organic material Breakdown of dead organisms, feces, fallen leaves & other organic refuse by bacteria and fungi Improves soil texture Reservoir of minerals Importance of organic matter, cont. Topsoil, cont. Organisms 1 teaspoon of topsoil has 5 billion bacteria living with fungi, algae, protists, insects, earthworms, and nematodes Soil health as a global issue Lack of soil conservation Growing wheat Raising cattle Land exposed to wind erosion Drought Soil conservation and sustainable agriculture Maintaining healthy environment Production of food supply Economically viable farming industry Global Issues Fertility Erosion Irrigation Forestry destruction Fertilizer “Organic” fertilizers Manure, compost, fishmeal “Chemical” fertilizers Commercially manufactured N-P-K ratio Irrigation Most often the limiting factor in plant growth Issues US rivers reduced to trickles by diversions of water Soil becomes salty and infertile Erosion Topsoil - lost to water and wind erosion Precautions Trees as windbreaks Hillside crops Contour pattern Sustainable Agriculture Soil Reclamation Removal and storage of contaminated soils New method: phytoremediation Biological, nondestructive cheap Nitrogen Fixation N2 N2 Atmosphere (gas) (gas) Soil Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria NH3 (ammonia) H+ (from soil) NH4+ (ammonium) Denitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria NO3(nitrate) NH4+ Ammonifying Bacteria Organic material (humus) Root Soybean Root Nodule N fixation by Rhizobium bacteria Symbiotic relationship between nitrogen-fixing bacteria and legumes Bacteroids inside nodules form Mycorrhizae and Plant Nutrition Symbiotic relationship Mycorrhizal fungus gets sugars from the plant In return, mycorrhizal fungus provides better absorption of water and minerals for the plant Ectomycorrhizae versus Endomycorrhizae Unusual Adaptations Epiphytes Grows on branches and trunks of trees Staghorn ferns, orchids Parasitic Plants Absorbs sugars and minerals from living hosts Mistletoe, dodder, and Indian pipes Carnivorous Plants Photosynthetic, but obtain minerals and nutrients by killing insects and other small animals Venus’ flytraps, pitcher plants, sundews