* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a Pacemaker?
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
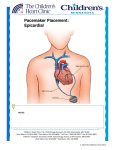
What is a Pacemaker? A pacemaker is a small device that is implanted in the chest to keep the heart rate from going too slow. It is made out of the generator or battery and connected to the leads or wires. The generator is the battery but it is also the “brains” of the pacemaker. The leads hook into the generator after they are placed into the heart muscle. There are several types and sizes of leads and the cardiologists who places the pacemaker typically chooses which leads to use. It may depend on the size of the veins, size of the heart, costs etc. Some people have only one lead, but more commonly there are two leads. One lead usually goes into the top part of the heart called the atrium. The second lead goes into the bottom chamber of the heart called the ventricle. A third lead may be placed into the left ventricle or coronary sinus in individuals that have heart failure or have had an AV node ablation. Your own heart can still beat on its own if it is able too but the pacemaker is there in case it gets too slow. It will send energy thru the leads that pace the heart muscle and cause it too beat. Many times the pacemaker is set at 60 beats per minute so the heart rate will never go slower than that. There may be reasons for it to be set a little slower than 60 or a little higher as well. Your cardiologist will determine the settings and they can be changed very easily. Will the Pacemaker prevent abnormal heart rhythms or other heart problems? No, the pacemaker will not prevent any abnormal heart rhythms. However, it will allow medicines to be given, that otherwise would have made the heart rate too slow, so the abnormal ryhthm may be treated. A pacemaker does not prevent a heart attack or a stroke. What are the risks for getting a Pacemaker? Having a pacemaker placed is a relatively safe procedure and is usually tolerated even at very advanced ages. The main risks are listed below: -Infection of the pacemaker pocket -Allergic reaction to dye or anesthesia that is given -A hematoma or pocket of blood\fluid that develops under the skin but over the pacemaker. This happens more commonly when people are on blood thinners. -Damage to blood vessels or nerves around the pacemaker -Collapsed lung -Puncture of the heart muscle which can be life threatening (this is very rare) What is the procedure like? The procedure usually last around 2 hours but may be shorter or longer depending on how many leads are placed into the heart. It usually does not require general anesthesia but rather a sedative to help keep you relaxed and comfortable. A small incision is made usually on your left upper chest under the collarbone that is about 2 inches long. Then the leads are placed into your heart through a vein. Once in place and functioning well, they are connected to the generator. The incision is closed. A chest x ray is done at this point to see how the leads look on x ray and make sure there is no collapsed lung. At this time, usually you are taken to your room where you recover and stay overnight. The next morning another chest x ray is performed and the pacemaker is checked through a computer. If everything looks good, at that point most patients are able to be discharged home. Are there restrictions after getting a pacemaker? For about 4 weeks your cardiologist may ask you not to do any heavy lifting. You may also be asked not to raise your arm above your shoulder for about 4 weeks. After that there are no physical restrictions. Can I still use electronics after my pacemaker? Absolutely. There are actually very few things now that interfere with pacemakers. Most household appliances have no significant interference with the device. Working on car engines or with some tools may have some risks to the pacemaker. If there is a question about a certain item, please refer to the Medtronic (one of the commonly used pacemaker companies) electromagnetic compatability guide. You may also refer to the guide from your pacemaker company which is usually on their website. What is the follow up for a pacemaker? Usually a wound check is scheduled in the office about 7-10 days after the pacemaker is placed. That is a good time to ask any questions you may have as well. After that, the pacemaker is usually checked every 3-6 months either by phone or with a wireless device the company provides you after the procedure. the checks may be done in the office or in your home. The wireless device should be plugged into the phone jack at your house to send a transmission. Cell phone capabilities may be available as well. Most cardiologists require follow up in the office at least once a year but it may be more frequent than that it there are other heart problems that need to be followed as well.