* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
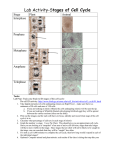
Mitosis vs. Meiosis Meiosis Mitosis • Non-reproductive cells • One parent cell makes 2 GENETICALLY IDENTICAL daughter cells • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase • EXACT COPIES with same # of chromosomes • Reproductive cells only (gametes) • One parent cell makes 4 GENETICALL DIFFERENT daughter cells with HALF the number of original chromosomes • Prophase 1, Metaphase1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1 • Prophase 2, Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2, Telophase 2 • PROPHASE 1 CROSSING OVER • ANAPHASE 1-> HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS SEPARATE • ANAPHASE 2 SISTER CHROMATIDS SEPARATE Cancer • Accounts for 1 in 4 deaths in developed countries • More than 100 different forms of cancer • Lung cancer=1 in 17 of all deaths in Britain in the 1990’s • Most common cancer in menlung • Most common form of cancer in women-breast Cancer • A disease that is the result of uncontrolled mitosis • Tumor-irregular mass of cells created by uncontrolled mitosis Origin of Cancer • Caused by changes in genes that control cell division • Mutation- a change in any gene • Not unusual • Most mutated cells are either crippled in some way that results in their early death or they are destroyed by the body’s immune system • Cancer cells bypass both these fates of mutated cells • Oncogene- term for mutated gene that causes cancer • Onkos in Greek means “mass” or “Bulk” Cancer • Although mutation may have occurred in one cell, it can be passed down to all of this one cells’ descendents • By the time it is detected, a typical tumor consists of about a thousand million cells • Mutagen • A factor that brings about any mutation • Things can be described as mutagenic • Carcinogen • Any agent that causes cancer • These can be described as carcinogenic • Some mutagens are carcinogenic • Factors that increase mutation rates (thus cancer) are as follows: 1. Ionizing Radiation 2. Chemical 3. Viral Infections 4. Hereditary predisposition Ionizing Radiation • X-rays, gamma rays, particles of a decaying radioactive element • Creates the formation of damaging ions inside cells that break DNA strands • UV light also breaks the DNA strands (but it does not cause the formation of ions) • Depletion of the ozone layer is becoming a concern • Leads to more UV radiation hitting Earth’s surface=increase risk to skin cancer Chemicals • Chemical compounds found in many consumer products • 25% of all cancers in developed countries are caused by the carcinogens in tar of tobacco smoke • Certain dyes (aniline) are well-known carcinogens Viral Infections • Viruses are genetic material and protein • Cancer viruses are estimated to cause 15 to 20 percent of all cancers in humans • Viruses that cause cancer usually carry oncogenes, or regulatory genes that can become oncogenes • The tumor viruses change cells by integrating their genetic material with the host cell’s DNA via a permanent insertion mechanism • This differs depending on whether the nucleic acid in the virus is DNA or RNA • In DNA viruses, the genetic material can be directly inserted into the host's DNA • RNA viruses must first transcribe RNA to DNA and then insert the genetic material into the host cell's DNA. Viruses and Cancer • DNA Viruses • RNA Viruses • The Epstein-Barr virus has been linked to Burkitt's lymphoma • Human T lymphotrophic virus type 1 (HTLV-I), a retrovirus, has been linked to T-cell leukemia • Infects B cells and epithelial cells • Causes mononucleosis, but can also cause a few different types of lymphoma and nasopharyngeal cancer • The hepatitis B virus has been linked to liver cancer in people with chronic infections • Human papilloma viruses have been linked to cervical cancer • The hepatitis C virus has been linked to liver cancer in people with chronic infections Hereditary disposition • Genetic link based on studying patterns in family members • Disease itself is not inherited but susceptibility to the factors that can cause the disease are inherited • Some forms of cancer are believed to be caused by the inheritance of one faulty gene • Example: Retinoblastoma…caused by error on chromosome 13 • Starts in both eyes during childhood and spreads to brain causing blindness and death if left untreated Tumors • Small groups of tumor cells are called primary growths • 2 types • Benign tumors • Tumors that do not spread from site of origin • They can compress and displace other tissues, causing discomfort and even death • Warts, ovarian cysts, brain tumors • Malignant (cancerous) tumors • Dangerous • Spread throughout the body, invading and destroying other tissues • Interfere with normal functioning of the area they have started to grow • Mutated cells break off the tumor and enter either the blood or lymph via vessel formation and spread all over the body creating secondary growths • METASTASIS is the spread of cancer from the origin to other parts of the body • most dangerous form of caner…can be very difficult to find secondary growths and remove them • Both benign and malignant tumors involve a huge drain on the human body due to the high demand for nutrients that is created by the rapid and continual cell division Stem Cells • Cell that can divide an unlimited number of times by MITOSIS • After division, each new cell has potential to: 1. Remain stem cell 2. Differentiate into specialized cell Stem Cell Therapy • Introduction of new adult stem cells into damaged tissue to treat disease or injury • Example: • Bone marrow transplant • Future goals of SCT: • Treat: • Diabetes • Nerve and muscle damage • Brain disorders • New tissue and organ growth