* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
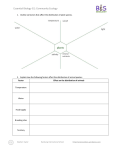
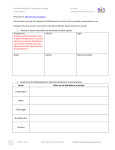
Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 1. Outline six factors that affect the distribution of plant species. 2. Explain how the following factors affect the distribution of animal species: Factor Effect on the distribution of animals Temperature Water Food Supply Breeding sites Territory Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 3. Explain the following interactions between species, giving two examples of each: Herbivory Explain: e.g. 1: Predation Explain: e.g. 1: Intra-specific competition e.g.2: Explain: e.g. 1: Stephen Taylor e.g.2: Explain: e.g. 1: Mutualism e.g.2: Explain: e.g. 1: Parasitism e.g.2: Explain: e.g. 1: Inter-specific competition e.g.2: Bandung International School e.g.2: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 4. Explain what is meant by the niche concept. 5. Give an example of two species in their niches: Example 1: Ocellaris amphiprion (ocellaris clownfish) Habitat: Nutrition: Interactions: Predators: Reproduction: Other info: Example 2: Habitat: Nutrition: Interactions: Predators: Reproduction: Other info: 6. Distinguish between fundamental and realized niches. 7. Using examples, explain the consequences of environmental change on a species with : A narrow niche: Stephen Taylor A broad niche: Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 8. Outline the method and importance of GF Gause’s paramecium experiments. (http://www.ggause.com/gfg05.htm) 9. Explain the competitive exclusion principle. 10. Using examples, explain how competitive exclusion can lead to: a. The removal/ replacement of one species from a niche. b. Niche partitioning 11. Annotate the diagrams below to show how random sampling and quadrats can be used to estimate the population of a plant species in a given area. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 12. Why is it important to ensure that selection of sample sites is random? 13. Outline some simple methods for generating random coordinates or otherwise ensuring that selection of a sample site is random. 14. How would the researcher ensure that their data are reliable? 15. How could the quadrat method be used to compare the population sizes of two plant species in one area? 16. The data collected can be used to compare the populations of two or more species. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology Species A B 12 7 Percentage cover in each quadrat (±2%) 34 32 45 12 34 46 12 9 23 5 4 12 5 8 mean STDEV 54 2 a. Calculate the mean and standard deviation of each set of results. b. What does the standard deviation tell us about these data? c. Which statistical test could be used to determine the significance of any difference between the two populations? H0 = Confidence limit usually chosen in Biology: d. The value of t was calculated as 3.995. Use the t-table to determine the significance of the results. n= Degrees of freedom (n-2) = Critical value = Is ‘t’ greater than or less than the critical value? Therefore reject/ accept H0. There is / is no significant difference in distribution of species A and species B. Can you also complete this using Excel? 17. What is the function of a transect? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 18. Explain how a transect would be carried out to correlate the distribution of a species with and an abiotic variable. 19. Give some examples of transects that you might carry out. Biotic Variable Abiotic Variable Vs. Vs. Vs. Vs. 20. What are some graph types that could be used to present the data collected in a transect? Sketch them. 21. Define biomass. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology G1: Community Ecology 22. Suggest some reasons for studying the biomass of an ecosystem. 23. Outline one method for estimating the biomass of different trophic levels of an ecosystem. 24. How do researchers ensure both minimal environmental impact and maximal reliability of results? 25. What are some of the ethical concerns associated with measuring biomass? 26. Explain why biomass is generally low at higher trophic levels. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com