* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
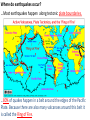
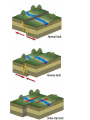
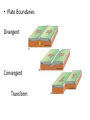
Earthquakes Part 1 • Earthquakes occur along faults Sometimes when you pull on a drawer, it opens smoothly. At other times, the drawer sticks shut. If you pull the drawer hard enough, the drawer suddenly flies open. This is how rocks along a fault act. A fault is a break or fracture in earth’s lithosphere (the crust and top of mantle), along which blocks of rock slide past each other. . Along faults, the rocks may slide past each other smoothly, or they may stick. Stress builds up until the rocks break free. A sudden release of stress in the lithosphere causes an earthquake. -An earthquake is a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault. Where do earthquakes occur? …Most earthquakes happen along tectonic plate boundaries. . …80% of quakes happen in a belt around the edges of the Pacific Plate. Because there are also many volcanoes around this belt it is called the Ring of Fire. . The best known fault on the Ring of Fire is the San Andreas Fault in California. Some quakes are also located on faults away from the plate boundaries and near hot spots in the lithosphere Faults are classified by how rocks move. Rocks along faults move differently depending on what kind of stress they are under. 1. Normal Faults: The block of rock above the fault slides down relative to the other block. -stress that pulls rocks apart causes this. 2. Reverse Faults: The block of rock above the fault moves up relative to the other block. -stress that presses rocks together causes this. 3. Strike-Slip Faults: Blocks of rocks move sideways on either side of the fault. - Horizontal stress causes this. The San Andreas Fault. . Over time, movement of rocks along normal and reverse faults can push up mountains and form deep valleys. Along strike-slip faults, rocks can be seperated by hundreds of miles. . Measuring Earthquakes To measure the strength of an earthquake, scientist use the Richter Scale. This measures the movement of ground near the quake. A scale from 1 to 10. Each number up means the quake is 10 times stronger than the last number. A 2 quake is 10 times stronger than a 1 quake. A 3 quake would be 10 x 10 (100) times stronger. A 6 quake would be 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 ( 100,000) times stronger than a 1 quake. • The Richter Scale . . • Plate Boundaries Divergent Convergent Transform