* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth*s Layers notes Part 2
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
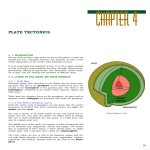
Earth’s Layers notes Part 2 LT.CE.7- I can explain what occurs at plate boundaries. • There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform. • 1) Convergent boundaries are where two plates are moving towards each other. This can result in uplift or in subduction. • Uplift results in mountain formation while in subduction the more dense plate goes under the less dense plate. The more dense plate gets pushed into the mantle where it melts and the buildup of new magma escapes to the surface as a hot spot or volcano. • Both uplift and subduction can cause earthquakes as well. • 2) Divergent boundaries are where two plates are moving in opposite directions or away from each other. Two main things that occur at this type of plate boundary is sea floor spreading and rift valleys. Sea floor spreading creates new sea floor and rift valleys make huge valleys in the earth that will sometimes fill up with water to create large lakes. • 3) Transform boundaries are when two plates are sliding and grinding against one another. This leads to lots of friction and very strong earthquakes. LT.CE.9- I can model the layers of the Earth and what happens between them. • Lithospheric plates or tectonic plates float on the Mantle. • Plates are less dense than the mantle, which allows them to float. • Plates are in constant motion; they move extremely slow. • The mantle has a current that pushes and pulls the lithospheric plates along with it. • The current in the mantle is a convection current. • Convection currents drive or power plate tectonics. • The mantle is a very viscous liquid. It is a very sticky liquid. • *Steps that make the plates move: 1) Warmer mantle rises up and sticks to the lithospheric plate. • 2) New warmer mantle rises up and pushes the cooling mantle to the side, which pulls the lithosphere with it. • 3) When the mantle completely cools it sinks back towards the core where it will be heated again. • Draw the diagram on the board. LT.CE.10- I can explain how interactions of the Earth’s layers affect the surface and organism on the surface. • The major result of interaction of Earth’s layers that affects organisms are earthquakes and volcanoes. These are both caused by plate tectonics which we have learned is a result of the layers interacting. • Both earthquakes and volcanoes have the potential to destroy habitat, homes, and kill organisms. • Volcanoes can also produce new land for organisms to live on and migrate to. • The interaction of the core, specifically the outer core, creates an electromagnetic field that protects organisms from radiation.