* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant organ lab book-2014
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
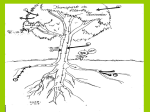
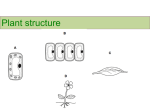
Plant Organs Utah State Core Curriculum Students will understand the relationship between structure and function of organs and organ systems. Standard 3 Objective 1 Describe the structure and function of organs. a. Diagram and label the structure of the primary components of representative organs in plants and animals (e.g., heart - muscle tissue, valves and chambers; lung - trachea, bronchial, alveoli; leaf - veins, stomata; stem - xylem, phloem, cambium; root - tip, elongation, hairs; skin - layers, sweat glands, oil glands, hair follicles; ovaries - ova, follicles, corpus luteum). b. Describe the function of various organs (e.g. heart, lungs, skin, leaf, stem, root, ovary). c. Relate the structure of organs to the function of organs. d. Compare the structure and function of organs in one organism to the structure and function of organs in another organism. e. Research and report on technological developments related to organs. Objective 2 Describe the relationship between structure and function of organ systems in plants and animals. a. Relate the function of an organ to the function of an organ system. b. Describe the structure and function of various organ systems (i.e., digestion, respiration, circulation, protection and support, nervous) and how these systems contribute to homeostasis of the organism. c. Examine the relationships of organ systems within an organism (e.g., respiration to circulation, leaves to roots) and describe the relationship of structure to function in the relationship. d. Relate the tissues that make up organs to the structure and function of the organ. e. Compare the structure and function of organ systems in one organism to the structure and function in another organism (e.g., chicken to sheep digestive system; fern to peach reproductive system). 2 Plant Tissue Systems There are ____ main types of plant tissues: 1. 2. 3. 1. Dermal: the dermal system has the epidermis which is the ___________ layer of the plant body. It makes the _______ of the plant. The epidermis has __________ through which gasses are switched with the atmosphere. The openings ate enclosed by _______ cells which change the size of the stomatal openings and control the _____ exchange. The epidermis is covered with a coating called the ________, which serves as a waterproof later and reduces water ______ through evaporation. 2. Vascular system: The system is made up of ____ types of conducting tissues. They are xylem, which conducts______, and dissolved mineral nutrients; and _______, which conducts food. 3. Ground System: The primary meristem in vascular plants that gives rise to the nonvascular tissues, such as cortex, pericycle, and pith. Within the seeds of angiosperms, it surrounds the procambium. Structure and Function of Plant Organs Plants generally have _______ organs: 1. 3. 2. 4. Roots: Hold the plant in _______ and they absorb ________ and minerals. Roots usually grow in the direction of __________ which is why they are most often found underground. They have _____ leaves. In short, the roots are in the ground and they give the plant water to help make its ____. All roots have a _______. The growing tip of roots is protected by the root cap consisting of concentric _______of cells surrounding the apical meristem where ____ root cells are produced. Label the Root: 1-8 Anatomy of root 3 1. Zone of differentiation: 2. Root hairs: 3. Zone of elongation: 4 Meristems 4. Procambium: 5. Ground: 6. Protoderm: 7. Apical 8. Root cap: R O O T L A B _____________________________ ______________________________ Three Main Types of roots: 1. Taproot: the first _______ to develop from a germinating seed, also called ________ root; a single, central, vertical root, which digs ______ into the soil searching for water. Taproots can also act as ______ roots, storing water and minerals for the plant to _____ off of. 2. Fibrous root: slender, branched __________ that look like fine string of _______. 3. Adventitious roots: roots that _________ from the stems or leaves of a ________. Alternate Roots-Not as Common: 4 4. Contractile roots: roots that can change in _________ and thickness, pulling shoots closer to the ground or deeper into the soil. 5. Root hairs: Can be found on any root system. They are tiny projections from the __________ cells of a root that extend ___________ the soil around the root. Stems: Stems are generally _________ ground, grow upward and have leaves. Can stems be different from one another? _________ Give me two examples: Phloem: It is a tissue that conducts synthesized ______ (glucose) substances to parts where needed by transporting the food made in the _______, down the stem and into the __________. Phloem-FLOWS _______ the plant! Xylem: acts as a protective _______ on the outside of the plant which helps prevent damage and _______ loss. It absorbs water and __________ through the roots and _________ them up the stem and into the leaves. Xylem transports _____ the plant! Vascular Cambium: one-cell-thick layer of tissue ________ xylem and phloem. Produces additional _________ tissues. Cork cambium: located outside the phloem, produces ________. Cork cells _________the epidermis in woody stems and roots, protecting the plant. Cork cells are _________ ________that provide protection and prevent water loss. HOW OLD IS THAT TREE? Each year a tree adds a layer of _______ to its trunk and branches thus creating the annual rings we see when viewing a cross section. New _______ grows from the __________ layer between the old wood and the bark. In the spring, when moisture is plentiful, the tree devotes its ________ to producing new growth cells. These ______ new cells are large, but as the summer progresses their size decreases until, in the fall, growth stops and cells ______, with no new growth appearing ______ the next spring. The contrast between these smaller old cells and _____ year's larger new cells is enough to establish a ______, thus making counting possible. Wide rings of certain species of trees were produced during _____ years and, inversely, narrow rings during ______ seasons. 5 1. How old is your tree? 2. How many dry seasons were there? 3. How many wet seasons were there? 2. Leafs: The leaf also contains veins and stomatas. Veins: _______ nutrients and water through the _______. Stomatas: are _____ in the epidermis of a leaf or stem through which gases and water vapor pass. Draw a picture of a stomata including their guard cells: 3. Flowers: Are responsible for one important function ______________. Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. __________ are types of plants that bare fruits and flowers. ___________ are usually both male and female, and are _______ colored to attract insects to help them carry _______ used for sexual reproduction. Not all flowers are colorful, though. These flowers usually use the _______ for pollination. Label and color the following flower: FLOWER ANATOMY: The ____________ is the tip of the stalk where the flower begins. The receptacle starts at the peduncle and ______ as a base to which all other parts of the flower are ____________. Sepals are leaf-like protective _________ of the bud that grow typically in an outer whorl. Petals are the inner whorl of ___________ 6 Pistils are the _________ organs. There can be one or _______. There are ______ parts of the pistil: o the stigma _________ the pollen and is sticky o the style _________ the stigma to the ovary o the ovary is where seeds ___________ Stamen are the _______ organs. The number of stamen per flower varies. There are ______ parts of the stamen: o the anther _________ pollen o the filament is the _______ which holds the anther. Investigation of Leaf Stomata Materials: Plant leaves, Clear fingernail polish, Clear cellophane tape (clear package sealing tape), Microscope, and Microscope slides Procedure: 1. Obtain a study leaf or other plant tissue. 2. Paint a thick patch of clear nail polish on the leaf surface being studied. Make a patch at least one square centimeter. 3. Allow the nail polish to dry completely. 4. Tape a piece of clear cellophane tape to the dried nail polish patch. (The tape must be clear. Do not use Scotch® tape or any other opaque tape. Clear carton-sealing tape works well.) 5. Gently peel the nail polish patch from the leaf by pulling on a corner of the tape and "peeling" the fingernail polish off the leaf. This is the leaf impression you will examine. (Only make one leaf impression on each side of the leaf, especially if the leaf is going to be left on a live plant.) 6. Tape your peeled impression to a very clean microscope slide. Use scissors to trim away any excess tape. Introduction: Scan the slide until you find a good area where you can see the stomata. Each stoma is bordered by two sausage-shaped cells that are usually smaller than surrounding epidermal cells. These small cells are called guard cells and, unlike other cells in the epidermis, contain chloroplasts. 1. Draw a stomata; labeling the Guard Cells and Epidermal Cells. 2. Estimate the number of stomata on your sample. ____________ 7 3. Make a hypothesis about the number of open stomata found in a plant kept in dark compared to a plant in the light. the Questions: 1. Will plants have more stoma open during the day than during the night? Why? 2. Can you see the chloroplasts inside the stomatas? Why or why not. Label & Color the LEAF anatomy: 8 Partner Questions 1. What two tissues are found within a vein? 2. What does the word "mesophyll" mean? 3. What two layers of the plant contain chloroplasts? 4. The outermost layer of cells: _________________________ 5. The waxy covering of the leaf.: _______________________ 6. These cells function to open and close stomata. _____________________ 7. Outer layer of the vein: ________________________ 8. Column like cells that lie just under the epidermis. ___________________ 9. Openings that allow for gas exchange. _________________________ 10. The stalk that connects the leaf to the stem. ______________________ 9 MONOCOTS VS DICOTS 10 Photosynthesis All organisms use ________ to carry out the functions of ___________. Photosynthesis: the process by which organisms _______ part of the energy in light and _____ it within organic compounds; energy transfer. They begin with the ______________ of light in the organelle found in plant cells and algae called ________________. Equation: Products: Draw photosynthesis and cellular respiration chart: Most ____________ or producers use photosynthesis to convert the energy in _____________, CO2, and H2O into _________ energy or food (________). Cellular Respiration: the process in which cells make ______ by breaking down organic molecules; food molecules are ___________ down to release energy for ________. C6H12O6 + 6O2→ 6CO2 + 6H2O + LIGHT Sugar oxygen ENERGY Products: 11 Plant Adaptations Adaptation: Desert Biome: Tropical Rain Forest: Grasslands: 12 Review 1. What is an angiosperm? 2. The flower attaches to what part of the plant? 3. Why are flowers brightly colored? 4. Name two mammals that might pollinate a plant. 5. If the petals of a flower are reduced or absent, how is the plant pollinated? 6. The female reproductive structures are called the: 7. Name the three parts of the pistil: 8. Where are the ovules stored? 9. Name the two parts of the stamen: 11. The ovary develops into what structure? 12. Define fruit. 13. Some flowers all, but have a very like rotting meat. flowers are are not brightly colored at pungent odor that smells How do you think these pollinated? Label the following diagrams: 13 Help Wanted! Different parts of plants do different jobs. Read the classified advertisements and help each of the plants parts listed below to find the right job. cambium guard cells phloem root cap sepals cuticle petals stamen pistil chloroplasts taproot xylem HELP WANTED HELP WANTED HELP WANTED Advertising Executive Colorful personality needed to advertise availability of pollen and nectar. Must have experience working with bees. Door Attendant Waiters/Waitresses Full-time positions available at entrance to stomates Deliver food to hungry plant cells. Work in busy roots, stems and leaves. Anchorperson Egg Farmer Interested in holding a plant in place? If you have experience digging deep in search of water, we're looking for you. No branching necessary. Female needed to manage egg production and receive pollen Chemist Person needed who can convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. Must wear a green uniform to work and enjoy working in the sun. Hardhats Bodyguard Help needed to protect buds. Apply before spring Construction workers. Drill for water. Protect other members of water-search team will drilling. Apply at root tip Pollen Production Assistant Help needed to produce pollen. Seasonal work only in the spring. 14 Outdoor Work Conductor Plumber Individual needed to carry water. Rapid advancement. Start at the roots and work up to the top! Protect and cover upper and lower leaf surfaces. Must be able to prevent water loss and seepage. Apply at the leaf. Vascular specialist needed to lay new plumbing each growing season. Experience making new xylem and phloem necessary. Potential for growth Write the name of the plant structure next to the job for which it is best qualified Advertisi ng Executiv e ____________________ ___ Anchorperso n __________________________ ____ Egg Farmer ____________________ ___ Chemist __________________________ ____ Bodygua rd ____________________ ___ Hardhats __________________________ ____ Pollen Producti on Assistant ____________________ ___ Conductor __________________________ ____ Outdoor Work ____________________ ___ Plumber __________________________ ____ Door Attendan t ____________________ ____ Waiter/Waitr ess __________________________ _____ 15 16