* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Variety in ecosystems - Grange Academy
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
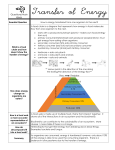
Variety in ecosystems Biodiversity – the number and variety of different species in any ecosystem. Species – a group of organisms capable of interbreeding to produce fertile offspring. The greater the biodiversity, the more stable an ecosystem is. A stable ecosystem has a wide range of species and food webs. Organisms are adapted to specific habitats e.g. Darwin’s finches on the Gallapagos Islands have evolved over a long period of time to fill specific niches on the different islands. They varied as to beak shape and size depending on their diet. Eats large seeds Eats cactus seeds and nectar Eats buds and fruits Eats flying insects Large chunky beaks are used for crushing seeds while small fine beaks show an insect based diet. Desert plants are adapted to survive in very dry conditions. They have specially adapted roots, reduced leaf surface area (spines) and thick waxy cuticles on the leaves. pmb jhs Effects of grazing High intensity grazing increases species diversity while very high or low intensity grazing will decrease diversity. Habitat destruction Destruction of the rainforest is rapidly reducing biodiversity and perhaps contributing to climate change. It destroys the habitats of many plants and animals many of which have yet to be studied. Pollution Air, soil and water are all affected by pollution as a result of the activities of man. It reduces biodiversity and causes harm to the environment. Behavioural adaptations Competition between organisms for resources such as food, water, light is common in both plants and animals. Woodlice in a choice chamber settle in damp and dark conditions which they prefer. In such conditions they avoid predators and do not lose water too quickly. To study them we control all variables except one at a time. They move more rapidly and randomly when conditions are unfavourable and slow down and rest more in preferred areas. pmb jhs