* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Brickell Academy Life Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
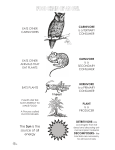
Questions/Main Ideas Essential Question How is energy transferred from one organism to the next? A food chain is a diagram that represents how energy in food molecules flow from one organism to the next. starts with a producer/autotroph (plant) = makes own food (energy from sun) primary consumer/heterotroph eats producer (zooplankton)= must get energy from eating other organisms secondary consumer (fish) eats primary consumer tertiary consumer (sea lion) eats secondary consumer quaternary consumer (shark) eats tertiary consumer herbivore = eats only plants omnivore = eats plants and animals carnivore – eats only animals What is a food chain and how does it show the transfer of energy? ** arrows point in the direction of the one doing the eating/the direction of the energy flow** Prey Predator How does energy change as organisms are eaten? Decomposers Quaternary Consumers 0.01% Tertiary Consumers 0.1% Secondary Consumers 1% Primary Consumers 10% Producers 100% How is a food web a more accurate representation of an ecosystem? How do decomposers fit into a food web? Summary A food web is made up of multiple food chains that interact together. It shows all of the interactions in an ecosystem and the biodiversity. Biodiversity can contribute to the sustainability of an ecosystem. More diverse = more stable if there is a change. Heterotrophs that get their energy from breaking down dead things. Examples: bacteria and fungus. As organisms are consumed, energy is transferred; however, only about 10% of the energy is able to be used the consuming organism. There is a balance in all ecosystems due to the transfer of energy.