* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
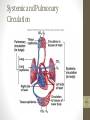
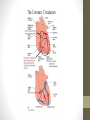
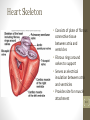
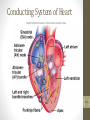
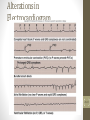
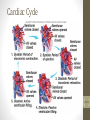
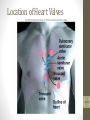
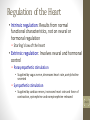
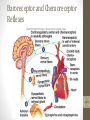
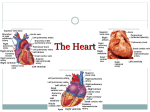
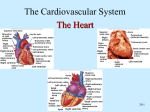
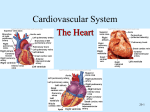
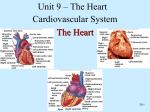
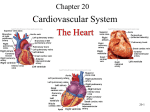
Cardiovascular System 2 Circuits of the Blood There are 3 circuits: 1. Systemic Circulation • From the left ventricle to the aorta and on to the body • Back to the heart via the superior and inferior vena cava to the right atrium 2. Pulmonary Circulation • From right ventricle to the pulmonary trunk, on to the pulmonary (left and right) arteries and to the lungs • Back to the heart via the (left and right) pulmonary veins 3. Cardiac/Coronary Circulation • Supply needs of the heart itself • Arteries go to the heart branching off of the aorta • Valveless veins return to directly to the right atrium Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation 20-3 Heart Skeleton • Consists of plate of fibrous connective tissue between atria and ventricles • Fibrous rings around valves to support • Serves as electrical insulation between atria and ventricles • Provides site for muscle attachment 20-5 Conducting System of Heart 20-6 Electrical Properties • Resting membrane potential (RMP) present • Action potentials • Rapid depolarization followed by rapid, partial early repolarization. Prolonged period of slow repolarization which is plateau phase and a rapid final repolarization phase • Voltage-gated channels 20-7 Action Potentials in Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle 20-8 SA Node Action Potential 20-9 Refractory Period • Absolute: Cardiac muscle cell completely insensitive to further stimulation • Relative: Cell exhibits reduced sensitivity to additional stimulation • Long refractory period prevents tetanic contractions 20-10 Electrocardiogram • Action potentials through myocardium during cardiac cycle produces electric currents than can be measured • Pattern • P wave • Atria depolarization • QRS complex • Ventricle depolarization • Atria repolarization • T wave: • Ventricle repolarization 20-11 Cardiac Arrhythmias • Tachycardia: Heart rate in excess of 100bpm • Bradycardia: Heart rate less than 60 bpm • Sinus arrhythmia: Heart rate varies 5% during respiratory cycle and up to 30% during deep respiration • Premature atrial contractions: Occasional shortened intervals between one contraction and succeeding, frequently occurs in healthy people 20-12 Alterations in Electrocardiogram 20-13 Cardiac Cycle • Heart is two pumps that work together, right and left half • Repetitive contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of heart chambers • Blood moves through circulatory system from areas of higher to lower pressure. • Contraction of heart produces the pressure 20-14 Cardiac Cycle 20-15 Events during Cardiac Cycle 20-16 Heart Sounds • First heart sound or “lubb” • Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole • Second heart sound or “dupp” • Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer • Third heart sound (occasional) • Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles and detected near end of first one-third of diastole 20-17 Location of Heart Valves 20-18 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) • Average blood pressure in aorta • MAP=CO x PR • CO is amount of blood pumped by heart per minute • CO=SV x HR • SV: Stroke volume of blood pumped during each heart beat • HR: Heart rate or number of times heart beats per minute • Cardiac reserve: Difference between CO at rest and maximum CO • PR is total resistance against which blood must be pumped 20-19 Factors Affecting MAP 20-20 Regulation of the Heart • Intrinsic regulation: Results from normal functional characteristics, not on neural or hormonal regulation • Starling’s law of the heart • Extrinsic regulation: Involves neural and hormonal control • Parasympathetic stimulation • Supplied by vagus nerve, decreases heart rate, acetylcholine secreted • Sympathetic stimulation • Supplied by cardiac nerves, increases heart rate and force of contraction, epinephrine and norepinephrine released 20-21 Heart Homeostasis • Effect of blood pressure • Baroreceptors monitor blood pressure • Effect of pH, carbon dioxide, oxygen • Chemoreceptors monitor • Effect of extracellular ion concentration • Increase or decrease in extracellular K+ decreases heart rate • Effect of body temperature • Heart rate increases when body temperature increases, heart rate decreases when body temperature decreases 20-22 Baroreceptor and Chemoreceptor Reflexes 20-23 Effects of Aging on the Heart • Gradual changes in heart function, minor under resting condition, more significant during exercise • Hypertrophy of left ventricle • Maximum heart rate decreases • Increased tendency for valves to function abnormally and arrhythmias to occur • Increased oxygen consumption required to pump same amount of blood 20-24