* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
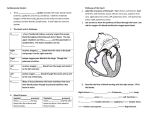
The Circulatory System http://www.sciencefinder.co.uk The Circulatory System You will learn the following Transport system needed (why?) Functions of blood (3) Composition of blood (4) Www.kidshealth.org For video on the circulatory system. Types of blood vessels (3) Differences between arteries and veins (3) What capillaries do. Structure of the heart (5 labels and explain) The main blood vessels of the heart (4 and function) Average pulse rate and how to measure it. How the heart pumps blood (7 points more honours) http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Find out from the video (1) The size of the heart? (2) Two types of blood vessels (3)The number of chambers of the heart (4)What the blood picks up at the lungs (5)What the blood gets rid of at the lungs (6)What causes blood pressure. http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Function: To transport materials around the body Oxygen Carbon dioxide Digested food Hormones Waste chemicals - urea Heat http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Compostion of Blood ( what blood is made up of) A liquid called plasma Red blood cells White blood cells Platlets http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Composition of Blood Plasma: This is the liquid part of the blood It carries heat helping to keep body temperature at 370C It carries dissolved substances such as CO2, hormones e.g. Insulin and wastes e.g urea. http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Composition of Blood Red blood cells Doughnot shaped Red pigment called haemoglobin which carries oxygen in the blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen.http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Composition of Blood White Blood cells Fight disease Produce antibodies to fight bacteria etc. Gobble up harmful bacteria etc. http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Composition of Blood Platelets Fragments of larger cells. Help clot the blood and seal wounds. What is haemophilia? http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk There are THREE types of blood vessels ARTERIES carry blood away from the heart Thick, muscular, stretchy wall narrow central tube http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk VEINS carry blood towards the heart thin walls with little muscle wide central tube have valves http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk CAPILLARIES carry blood between arteries and veins wall only one cell thick very narrow central tube http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Thick muscular walls Divided into 4 chambers Right side pumps blood to lungs Left side pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs to ALL parts of body http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Right Atrium Left Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle The heart is divided into FOUR chambers http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk AORTA PULMONARY VEIN http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk The heart has four major blood vessels http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Red blood cell collects OXYGEN in the lungs 2 The oxygenated cell travels along the pulmonary vein to the LEFT ATRIUM http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Oxygenated blood carried to ALL parts of body via the AORTA http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Deoxygenated blood carried back from all parts of body via the VENA CAVA Deoxygenated blood sent back to the lungs for oxygen via the PULMONARY ARTERY http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Inside every cell oxygen is used in RESPIRATION to produce WATER + CARBON DIOXIDE + http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Draw a flow chart 1. 2. 3. Show the route of a red blood cell Starting at lungs and moving via heart to arm Leaving the arm and returning back to the lungs Labelled oxygenated blood cells (red), deoygenated blood cells (blue), the heart, lungs, arteries and veins http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk LUNGS Circulatory system Artery – red HEART Vein - blue ARTERY carrying oxygenated blood to leg VEIN carrying deoxygenated http://www.sciencefin blood back to heart der.co.uk Circulatory System Circulation Heart structure Visit www.worldofteaching.com http://www.sciencefinder.co.uk For 100’s of free powerpoints Double Circulation Right side Left side Deoxygenated blood from the body is returned to the heart to be pumped to the lungs Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the heart and is pumped to the body organs and tissues http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Pulmonary system – up to the lungs CARBON DIOXIDE Systemic – to the organs of the body http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk OXYGEN Structure of the heart http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk You need to be able to label all parts of the heart http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Blood from ? Blood from lungs right atrium ? valve Right ventricle Left ventricle – has a thicker muscle wall than right side – why? http://www.sciencefin RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE der.co.uk Body organs http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Blood to the ? Blood from ? Blood to the ? Blood from lungs right atrium Left atrium valve Right ventricle Left ventricle http://www.sciencefin RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE der.co.uk http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Beating heart – blood flow The valves prevent the backflow of blood. http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk How do the valves work? How many can you see? http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk out in Can you see the 4 valves? Atrium and ventricle muscles force the blood through and out of the heart http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk in VALVE between the atrium and ventricle Ventricle wall Ventriclehttp://www.sciencefin chamberder.co.uk Artery Capillary Vein Carry blood away from the heart Wall only one cell thick. Large lumen Small lumen No valves Usually have deoxygenated blood. Very elasticConnect arteries walls can stretch to veins Low pressure Leaky so that substances can Usually have pass out oxygenate blood http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Carry blood to the Haveheart. valves that No valves stop blood moving the wrong way Heart disease Arteriolosclerosis is a disease where the arteries harden or thicken. Caused by smoking and cholesterol in the diet. Leads to high blood pressure and http://www.sciencefin increased risk of heart der.co.uk attack. The Pulse Rate Pulse = throbing sensation due to pressure of blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps the blood. The average adult heart beats about 70 times per minute. It can be measured by taking your pulse rate for example at the wrist. Your pulse rate is a measure of how fit you are. http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Measuring your pulse rate Find your pulse at the wrist, neck or temple. Using a stop watch count the number of pulses in a minute. How would you show the effect of exercise ón pulse rate? What effect do you think exercise will have? http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk Do the gap fill exercise http://www.sciencefin der.co.uk