* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module I: About Chili Pepper
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
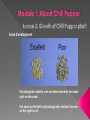
At the end of this lesson, you have learned to answer: 1. How chili pepper is a better crop than other vegetable crops like tomato, watermelon, etc.? 2. What chili pepper types are cultivated? 3. How many days chili pepper seed takes to germinate? 4. Describe the root system in chili pepper? 5. Which type of roots provide anchorage to the chili pepper plant? 6. Describe the shoot system in chili pepper? 7. What is boot stage and how can you identify this stage in chili pepper? At the end of this lesson, you have learned to answer 8. In how many days after germination the flowering initiation starts? 9. How can you identify flowering in chili pepper? 10. What is physiological maturity in chili pepper? 11. How can you identify physiological maturity in chili pepper? 12. In how many days chili pepper plant matures? 13. What is the optimum stage to harvest chili pepper? Chili pepper is a member of the nightshade family and originally a wild plant in southwestern Ecuador. The evolution of chili pepper under the pressures of cold and low temperatures imparted the ability to tolerate cold, soil toxicities, and freezing temperature more effectively to cultivated chili pepper plants than other vegetables. Wild Chili pepper Varieties of chili pepper are classified into 5 groups: • Ethnic Hot peppers • Chili pepper •Ethnic Sweet peppers •Ornamental and Bedding peppers • Sweet Bell peppers. Spice chili peppers are grown for the vegetable - long, fleshy skin used as human food or spices and condiment. Spice chili pepper Sweet peppers have sweet juicy flesh and are grown for making pepper sauces. Sweet peppers can also be used for salads or for making pickles. Sweet Pepper Germination At optimum temperature77 t0 86oF (25 to 300 C) and moisture, the chili pepper seed germinates in 4 to 6 days. When chili pepper seed is sown in moist soil, the seed swells due to moisture absorption. The seed coat breaks a small shoot (coleoptile) and a primary root (radicle) emerge. Stage 1 of Chili pepper Germination Initially the young seedlings take nutrients from the endosperm of the seed. Seedling Development The shoot (coleoptile) emerge from the ground and first leaf breaks through the tip. First Leaf Coleoptile Mesocotyle Seed Primary Root The mesocotyle grows during this period and a node is formed at the base of the coleoptile just below ground level. Secondary roots begin to grow from this node, 3 to 7 days after the plant emerges from the soil. Seedlings get the nutrients through these roots. Stage 2 of Chili pepper Germination Root system The chili pepper root system consists of 3 types of roots: • Primary roots • Secondary or Adventitious roots • Tap roots Primary roots These roots develop from the radicle and die subsequently. Root system Secondary or Adventitious roots These roots develop from the first node from the mesocotyle. These rots occupy 5 to 15 cm area in the soil around the base of the stem. Secondary roots of Chili pepper Adventitious roots are small, uniform, and form a small portion of the root system. Shoot system Leaves Node }Inter Node Stem Chili pepper shoot system consists of stem, leaves, nodes, and internodes during the vegetative stage. Leaves\nodes develop @ of one in 3 to 6 days. The plant remains in vegetative stage for 30 to 40 days during which all leaves (12 to 18) are formed. Chili pepper shoot Shoot system About at 6 to 10 days of flowering, the Plants become very green and healthy and initiate flowers. Chili pepper usually flowers 35 to 45 days. Flowering stage Shoot system Two days after the emergence of the flowers from the shoots, the flowers begin to open. The flowering can be observed from the white pollen from the anthers on the berry. The maximum flowering takes place on 3rd or 4th day. It takes 6 days for the whole inflorescence to complete flowering. Flowering in chili Seed Development The chili pepper seed is called pepper seed. The seed matures in 30 to 35 days after fertilization. Chili pepper seeds are round in shape but flat on both sides. Pepper seeds The seeds vary in color - red, brown, white, yellow, or cream and are with a dull or pearly luster. Seed Development Physiological maturity: Maximum total dry weight of the plant reaches at the physiological maturity. Uptake of nutrients also mostly cease at this stage. So, if there are problems like bird damage etc. it is advantageous to harvest the crop at this stage. As the seed moisture at this stage will be around 25 to 35%, proper drying of the seeds is important. Seed Development Physiological maturity can be determined by the dark spot on the seed. The seed on the left is physiologically mature; the one on the right is not. The cultivated pepper mature and get ready for dry in 100 to 140 days depending on the variety. The right time to harvest chili pepper is at the physiological stage of the plants or when the berry moisture content is below 45%. With this, the Lesson on Growth of Chili pepper Plant, and also the Module 1 - About Chili pepper concludes. If you want to check your understanding on about chili pepper, please click on “Exercise” button given above. The subsequent Modules in this course deal with the important insect pests that attack chili pepper crop. Click “Modules” button and select Module 2