* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid Disease and Hair Loss
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
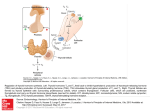
Thyroid Disease and Hair Loss Types of Hair Loss Generalized shedding More hair in drains, on brush No specific patches of loss or baldness Most common in thyroid disease Discrete patches of loss Associated with fungal infection or autoimmune alopecia Male pattern baldness Men and women Loss concentrated of temples and top of head Conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone Causes Untreated/Undertreated Thyroid Disease Hypo- or hyperthyroidism Thyroid gland unable to provide hormones for hair follicle’s proper metabolism Loss of necessary supply of proteins and amino acids Loss of ability to absorb vital minerals and vitamins Inability to grow properly Redirection of energy needed for hair growth to other parts of body Medication Side Effect Levothyroxine (Synthroid) According to patient information, may cause generalized hair loss Treatment for thyroid cancer Treatments Normalize thyroid levels May benefit from addition of T3 (Cytomel) or T4/T3 drug (Thyrolar, Armour) versus pure synthetic T4 (Synthroid) May take several months to see improvement Alternative supplements Evening primrose oil (EPO) Source of essential fatty acids Lysine supplementation (meat, fish, eggs) Aromatherapy of essential oils (thyme, cedar wood, lavendar, rosemary) Hair transplantation Treatments to Avoid DHT inhibitors (Propecia) Growth stimulators (Minoxidil) These medications have not been shown to be effective in patients with thyroid imbalances Eyebrow Loss More common in hypothroidism Primarily affects outer third of brow – may be completely absent Treatments Similar to head hair loss (thyroid meds, evening primrose oil, supplements) Transplantation (micrografts, single hair) Permanent makeup (tattoo) Eyelash Loss Hypo – or hyperthroidism Eyelash hair follicles have thyroid hormone receptors on their surface Uncommon to be the presenting sign in thyroid disease Rule out other causes trichotillomania DM vitiligo pernicious anemia Addison’s Treatments Similar to other treatments discussed Additional treatments FNS Nutrilash Mixture of vitamins, minerals and amino acids Latisse Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution Side effects: increased brown pigmentation of iris, eyelid skin darkening, eye redness, itching) LiLash Prostaglandin analog Side effects: eyelid darkening, eye redness, itching