* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vacation Packet - Manhasset Schools
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
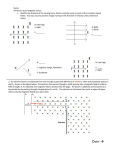
Name______________________________________ date__________ Vacation Homework 1. A balloon that is filled with a He is attached by a string of negligible mass to a small 0.02 kg object that is just heavy enough to keep the balloon from rising. The total mass of the balloon, including the helium, is 0.0060 kg. The density of air is ρair= 1.29 kg/m3 , and the density of helium is ρHe= 0.179 kg/m3 . The buoyant force on the 0.02 kg object is small enough to be negligible. (a) On the dot below that represents the balloon, draw and label the forces (not components) that act on the balloon. (b) Calculate the buoyant force on the balloon. If you need to draw anything other than what you have shown in part (a) to assist in your solution, use the space below. Do NOT add anything to the figure in part (a). (c) Calculate the volume of the balloon. d) Suppose the balloon was filled with sulfur Hexafluoride instead of He. ( ρSF= 6.8 kg/m Describe all of the changes in your force diagram. Explain your reasoning. 3) 2. The diagram shown above is a velocity selector, labeled region 1. It consists of two parallel conducting plates, with charges on the plates as indicated creating an electric field of magnitude E directed toward the top of the page. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B1 directed out of the page exists between the plates. The magnitude of the magnetic field can be adjusted so that only particles of a particular speed pass through the selector in a straight line. A radioactive source to the left of the selector emits charged particles, each having the same charge q and moving to the right in the plane of the page. The effect of gravity can be neglected throughout the problem. (a) i. Derive the equation v =E B1 region 1. for the speed v of particles that move in a straight line through ii. Some particles are emitted from the source with speeds greater than E B1 . Which of the following describes the initial path of one of these particles immediately after entering region 1 ? It curves toward the top of the page. It curves toward the bottom of the page. It curves into the page. It curves out of the page. It moves in a straight line. Explain your reasoning. A constant magnetic field of magnitude B2 directed into the page is now added in region 2 to the right of region 1, as represented in the figure below. Suppose a particle leaves the radioactive source, travels through region 1 in a straight line, and enters region 2. For each of the following, express algebraic answers in terms of E, B1 , B2 , q, and fundamental constants, as appropriate. (b) Determine an expression for the initial magnetic force on the particle in region 2 and state its direction. (c) Describe the changes, if any, in the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force as the particle moves in region 2. (d) Describe the path of the particle in region 2. (e) Derive an expression for the charge-to-mass ratio q m of the particle. Specifically note any quantities not previously defined that are included in your answer. N = 1.5 3. (10 points) A triangular glass prism has a beam of red light of wavelength 6.65x10-7 m in air incident at an angle θ1 with the normal. The glass has index of refraction n = 1.5 for the red light. When θ1 = 40o the beam emerges on the other side of the prism at an angle q4 (a) Calculate the angle of refraction θ2 at the left side of the prism, and θ4 (b) Using the same prism, describe a change to the setup that would result in total internal reflection of the beam at the right side of the prism. Justify your answer. (c) The incident beam is now perpendicular to the surface. The glass is coated with a thin film that has an index of refraction n f = 1.4 to reduce the partial reflection of the beam at this angle. i. Calculate the wavelength of the red light in the film. ii. Calculate the minimum thickness of the film for which the intensity of the reflected red ray is near zero. 5. (10 points) The circuit above has a battery with voltage E, connected to two long, straight, parallel wires, which in turn are connected to four resistors with resistances given in the figure above. Assume that any other resistances in the circuit are negligible. Express all algebraic answers to the following parts in terms of the given quantities and fundamental constants. (a) Derive an expression for the total resistance of the circuit. (b) Derive an expression for the power dissipated in this circuit. Assume that any magnetic fields result only from the currents in the two long wires. (c) What is the direction of the magnetic field, if any, at point P, which is in the plane of the page Explain your reasoning. (d) What is the direction of the force, if any, on the bottom wire due to the current in the top wire? Explain your reasoning. 6. (10 points) A train runs on a steam engine with a power output of 6.5x106 W and an efficiency of 11 percent. (a) Calculate the rate at which heat is being delivered to the steam engine. Suppose the gas in another heat engine follows the simplified path ABCDA in the PV diagram below at a rate of 4 cycles per second. 0.4 0.80 1.20 (c) i. What does the area bounded by path ABCDA represent? Explain your reasoning. ii. Calculate the power output of the engine. (d) Indicate below all of the processes during which heat is added to the gas in the heat engine. Explain your reasoning for each: AB BC CD DA