* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 28.1 Levels of Organization
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
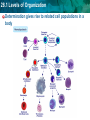
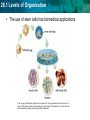
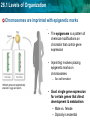
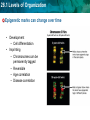
28.1 Levels of Organization LEQ: How do cells become committed to specialized functions in bodies? • Key terms – stem cell, cell determination, • Reading – 28.1, 5.5, 8.6 (eukaryotic gene regulation) • Lab due 5/3 • Test/note cards Friday 5/4 28.1 Levels of Organization • Activator: – Complete epigenome survey 28.1 Levels of Organization Stem cells add new cells to a body when they divide • Stem cells have the ability to – divide and renew themselves via mitosis - Stochastic (top) - Asymmetric (bottom) – Daughter cells can specialize in biological tasks 28.1 Levels of Organization Specialized cells of the body develop from stem cells 28.1 Levels of Organization A stem cell divides and forms specialized populations of cells • Cell Determination is committing to become one cell type. • Factors affecting determination: • Cell position in the body • Signaling • Gene expression 28.1 Levels of Organization Determination gives rise to related cell populations in a body 28.1 Levels of Organization • The use of stem cells has biomedical applications First, an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell in a petri dish. The egg divides, forming an inner cell mass. These cells are then removed and grown with nutrients. Scientists try to control how the cells specialize by adding or removing certain molecules. 28.1 Levels of Organization Summary: • What are the characteristics of stem cells? • Explain how a stem cell’s fate is “determined,” what factors influence the future jobs these cells will perform? • Discuss the potential to use stem cells in medical therapy – Is using human embryos essential for medical therapy? Why or why not? 28.1 Levels of Organization Chromosomes are imprinted with epigenetic marks • The epigenome is a pattern of chemical modifications on chromatin that control gene expression • Imprinting involves placing epigenetic marks on chromosomes – Sex cell formation • Goal: single gene expression for certain genes that direct development & metabolism – Male vs. female – Diploidy is essential 28.1 Levels of Organization Changes to the epigenome alter how cells use their DNA – Histone modifications – chemically modify “tails” – DNA methylation – CpG islands: CG rich DNA 28.1 Levels of Organization Epigenetic marks impart a genetic memory on cells “determining” their fate • Genes can be switched on or off permanently 28.1 Levels of Organization Changes in epigenetics can result in disease • (A) previously unmethylated tumor suppressor gene such as p53 becomes methylated suppressing gene expression • (B) A protooncogene is demethylated, allowing TFs express the protein product. 28.1 Levels of Organization Epigenetic marks can change over time • Development – Cell differentiation • Imprinting – Chromosomes can be permanently tagged – Reversible – Age correlation – Disease correlation 28.1 Levels of Organization Summary: • A cell has undergone determination to become an endocrine gland cell. If it is transplanted to a leg muscle, what do you think will happen to this cell?