* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses and Bacteria
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
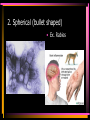
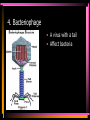
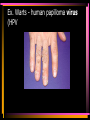
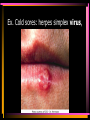
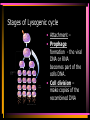
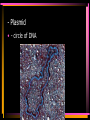
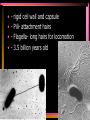
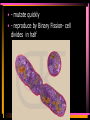
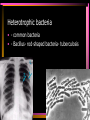
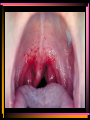
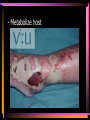
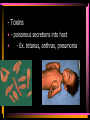
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease • Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host’s tissues • Can be transmitted to others • Pathogen – microorganisms that cause disease Pathogens cause disease by: • Enter host body (mouth, open wounds ,eyes) • Adhere to specific host cells • Invade/colonize host tissues • Inflict damage to tissues 5 agents of infectious disease • • • • • Viruses Fungi Bacteria Protists worms 2 Categories of infectious disease • Emerging infectious disease • Re-emerging infectious disease Emerging infectious disease • Have not occurred in humans before • Have occurred in humans before, but affected only small numbers of people in isolated place (AIDS, Ebola) • Due to environmental changes Re-emerging infectious disease • Once were a major health problem, then declined dramatically … • Again becoming health problems (malaria, tuberculosis) • Due to drug resistance, lack of vaccination Emerging Re-emerging Endemic Flu Pandemics: 1918 Spanish Flu • Killed up to 50 million people worldwide • Killed more Americans than all the wars this century combined The Bird Flu (H5N1): Could this virus cause the next pandemic? •Highly pathogenic •Since 2003 this the “bird flu” virus has caused 172 deaths worldwide. •Humans that contracted the virus were in close contact with infected birds. Viruses • Characteristics of Viruses • - is it alive? • - not cells • - parasites • - replicate themselves • - found everywhere • - DNA or RNA inside • - protein coat- capsid • - specific- species and cells Classification of Viruses : A. Shape • ROD Shaped • Ex. Tobacco Mosaic Virus 2. Spherical (bullet shaped) • Ex. Rabies Spherical: • Influenza 3. Polyhedral • Ex. Adeno virus • Causes respiratory illnesses, pink eye, digestive illnesses 4. Bacteriophage • A virus with a tail • Affect bacteria - B. Classified by their Vector • - organism that carries virus C. Classified by the disease it causes • Ex. Rhinovirus – group of viruses that cause the common cold. Ex. Smallpox • No longer a threat due to vaccination by Edward Jenner Ex. Chicken pox Ex. Warts - human papilloma virus (HPV Ex. Cold sores: herpes simplex virus, Ex. Polio Viruses and Disease • - Table 21-1 • Immunity – white blood cells and your bodies antibodies. There is no cure for a virus • Vaccines – inject inactive virus to produce antibodies. White blood cells in action - Phagocyctes - Interferon • - inhibits virus replication • - body produces when attacked Viral Replication • 100 new viruses every minute • Two cycles of replication: – 1. Lytic Cyclehost cell is killed. Stages of Lytic Cycle • 1. Attachment – • 2. Entry – Virus injects its DNA or RNA into the cell • 3. Formation – viral DNA or RNA replicates • 4.Lysis and release – cell bursts and releases newly formed viral cells. Stages of Lysogenic cycle • Attachment – • Prophage formation - the viral DNA or RNA becomes part of the cells DNA. • Cell division – make copies of the recombined DNA Bacteria Archaebacteria Eubacteria Characteristics • - unicellular- colonies or filaments salmonella E.coli - prokaryotes - Plasmid • - circle of DNA • - rigid cell wall and capsule • - Pili- attachment hairs • - Flagella- long hairs for locomotion • - 3.5 billion years old Life of a Bacterium • - found everywhere - reproduce rapidly - live in extreme conditions • - mutate quickly • - reproduce by Binary Fission- cell divides in half - some don't need oxygen (Botulism) • - Pathogenic • - harmful to man • Water treatment vs Friendly - useful to man Four groups of Bacteria – consumer types chemosynthetic photosynthetic Heterotrophic bacteria • - common bacteria • - Bacillus- rod-shaped bacteria- tuberculosis - Coccus • - round bacteria- strep throat - Spirillum • - spiral bacteria- syphilis - Metabolize host - Toxins • - poisonous secretions into host • - Ex. tetanus, anthrax, pneumonia Chemoautotrophic bacteria • - nitrifying bacteria • - convert nitrogen to plants in soil Photosynthetic bacteria • - blue-green color • - contain chlorophyll • - autotrophs- makes own food and 02 Gleocapsa • Colony type • Gel sheath Oscillatoria • Filament • Moves in a wave like manner Lyngbya • Filament • Notice in a gel sheath Notoc • - blooms cause CO2 loss in water - antibiotics • - penicillin, ampicillin, omoxycillin, tetra cycline - immune system • - white blood cells