* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measuring Earth
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
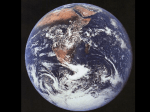
Topic 2: Measuring Earth How can we determine the shape of the Earth? What evidence do we have about the shape of the Earth? What are the parts or layers of the Earth? What is the true shape of the Earth? The true shape is an oblate spheroid. It is bulging at the equator and slightly flattened at the poles. What are the dimensions of the Earth? • 40,008 Km • 12,714 Km • 12,756 Km • 40,076 Km What evidence do we have that proves the Earth is round? • • Space photos – satellites in space take pictures which show the Earth to appear smooth & round. Motions of ships sailing towards the horizon – Ships sailing toward the horizon seem to disappear from bottom to top. What evidence do we have that proves the Earth is round continued? •Shape of Earth’s shadow during a lunar eclipse - The Earth casts a curved shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse. •Altitude of Polaris - Polaris remains fixed over the north pole but as a person changes latitude so does the altitude of Polaris. What evidence is there that the Earth is not perfectly round? • If the Earth was perfectly round the gravity measures would be that same, a person would weigh the same everywhere, but they don’t, objects weigh slightly more at the poles and slightly less at the equator. How would you describe the smoothness of Earth’s surface? • It is very smooth compared to its diameter. What are the outer spheres of the Earth? • Atmosphere- the layer of gases that surrounds the Earth. • Lithosphere- The layer of rock that forms the solid outer layer. • Hydrosphere- The layer of liquid water which lies between the atmosphere and the lithosphere. What are the characteristics of the atmosphere? • Composed mainly of gases (nitrogen & oxygen) • The least dense outer layer. • The atmosphere is layered (stratified) – Troposphere – Stratosphere – Mesosphere – Thermosphere • The boundaries between the layers are called pauses • All clouds and air traffic are located in the troposphere. What are the characteristics of the hydrosphere? • This layer makes up 70% of the Earth’s surface • This layer is thin, it is only 3.8 Km thick • Composed of the H2O (Hydrogen & Oxygen) • H2O is mainly oceans What are the characteristics of the lithosphere? • This layer is about 100 Km thick • It is divided into sections called plates • The upper portion of the lithosphere is called the crust. • Crust that is broken up and contains organic matter, it is called soil.