* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - California State University, Los Angeles
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
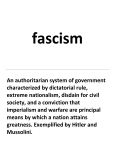
XX. World War II A. U.S. Foreign Policy 1. Russia a. 1919 U.S., Britain, France & Japan invaded Siberia b. hoped to destroy Bolsheviks & Russian Communism c. heavy losses on both sides d. U.S. refuses to recognize Russia i. Roosevelt to sell excess grain ii. USSR pays Russian debt of WWI 2. Slowed American imperialism a. allowed a rebellion in Cuba and a military coup b. recognized the new government c. offered them a loan & abrogated Platt Amendment i. in exchange was given a naval base at Guantanamo 3. Mexico threatened war in 1938 a. U.S. oil was unresponsive to government & exploitive b. Mexico nationalized U.S. oil companies c. U.S. refused to sell replacement parts for oil machinery d. Mexico agrees to pay for confiscated machinery e. Mexico closer to Germany & Japan who supplied parts B. Fascism begins 1. 1922 Benito Mussolini introduces Fascism to Italy a. previously a socialist, renounces old ties b. based new party on supremacy of old Roman Empire c. May 1935 invaded Ethiopia i. Britain sent fleet to Mediterranean but did not fight ii. League of Nations condemned action but was helpless iii. Congress passed Neutrality Act of 1935 a. prohibited all arms shipments to warring nations b. advised citizens to avoid travel in belligerents c. trying to avoid causes that led to WWI 2. Adolf Hitler in Germany a. corporal during WWI started National Socialism party b. German police imprisoned him in 1923 i. wrote philosophy of Nazism in Mein Kampf ii. wrote about racial purity & hatred of Jews iii. way of gaining political & economic control c. January 1933 Hitler becomes chancellor i. by March declares himself dictator ii. 1934 starts rearmament of Germany iii. set out to conquer Europe in a new German Empire 3. Spanish government collapsed in 1936 a. socialist government took over but face civil war b. Francisco Franco, Catholic Church & land owners i. Germany & Italy supported Franco’s revolt a. Germany tried new weapons & strategies i. air force gained experience ii. hand held machine guns & grenades iii. experimented with total war & bombed Guernica ii. Soviet Union supported rightful government iii. Americans fought on both sides a. Roosevelt extends Neutrality Act b. Communist party pulls out support c. Franco wins 4. German aggression a. started expansion in 1938 i. annexes Austria in March 1938 ii. September occupies Sudetenland (Czechoslovakia) iii. took the rest of the country by end of 1938 iv. August 23, 1939 Nazi-Soviet nonaggression pact a. planned to divide Poland between the two v. P.M. Neville Chamberlain offered appeasement vi. Britain & France entered treaty to protect Poland a. a week later Germany & Russia invaded Poland 5. Japanese aggression a. isolated industrial island i. needs natural resources ii. 1931 invades Manchuria iii. 1937 full China invasion b. 7/1939 U.S. cancels 1911 commercial agreement i. exerted political pressure on Japan to withdraw C. World War II 1. U.S. refused to enter another European war a. Roosevelt worried about German aggression b. sold Britain & France arms on cash & carry basis i. avoid upsetting U.S. economy with loans ii. avoided Germany attacking U.S. cargo shipments c. 1939 learnt Germany developing an Atomic Bomb i. Roosevelt authorizes the Manhattan Project 2. the "Phony War" a. nothing happened for another year b. G.B. sent a few divisions to France after Poland 3. Blitzkrieg (lightening war) a. 4/9/1940 Germany invades Norway & Denmark b. 3 weeks & Belgium, Luxembourg & Netherlands c. a week later they marched into France i. France defended a frontal assault with Maginot line a. large line of cannons facing Germany b. subway connecting them with supplies & troops ii. Germany avoided it by invading Belgium first iii. Maginot line was useless, cannons faced wrong way d. Germans advance to a few miles from Paris e. a few weeks later France surrendered 4. Roosevelt expands help to Britain a. Traded 50 destroyers for navel & air bases b. Congress gave $4 billion for new warships c. Selective Service Act, 1st peace time draft d. Germany bombs Britain in preparation for invasion e. Russia invades Finland f. Roosevelt wins reelection for third term g. lends Britain war supplies, Lend-Lease Act h. closes Italian & Germany consulates 5. Hitler makes first big mistake and attacks Soviet Union a. U.S. needs Soviet ally extends them Lend-Lease i. Americans were sending the supplies to allies ii. Germans American supply ships 2x faster than built 6. Japanese involvement a. U.S. exerts more pressure on Japan to stop aggression i. 9/1940 stops shipments of airline fuel & scrap metal ii. 3/1941 increases embargo to everything except oil iii. U.S. volunteers join Chiang Kai-Shek (Flying Tigers) b. Japan decides to invade French Indochina & south c. July 1941 Roosevelt freezes all Japanese assets in U.S. i. diplomatic relations break down ii. U.S. deciphers Japanese diplomatic code d. Japanese launch well orchestrated campaign in Pacific i. Dec. 7, 1941 attack Pearl Harbor, Philippines, Guam, the Midway Islands, Hong Kong & Malaya ii. new U.S. aircraft carriers on maneuvers out at sea e. Dec. 8, 1941 U.S. declares war on Japan f. Dec. 11, 1941 Germany and Italy declare war on U.S. D. U.S. in WWII 1. Arcadia Conference, Dec. 22, 1941 a. Churchill discusses war with Roosevelt in D.C. 2. War Production Board a. gave contracts to businesses with guaranteed profits b. no anti-trust cases in war related industries c. profits increased in almost all businesses & farms 3. National War Labor Board a. sets wages & hours & monitors work conditions b. President could seize any plant that did not cooperate c. allowed some wage increases because of inflation d. 1943 John L. Lewis called national coal strike i. Roosevelt orders nationalization of mines ii. Lewis reevaluates position & calls off strike 4. Roosevelt started Office of Price Administration (OPA) a. regulated all resources needed for war b. set rations & checked inflation i. rubber, sugar, gasoline, silk & meat ii. received coupons & encouraged not to use c. rush to create new synthetic substitutes 5. Roosevelt and Japanese American citizens a. animosity towards Japanese spread to those in U.S. b. West coast urged investigation of Japanese Americans i. worried about fifth column ii. War Department investigated & found no real threat c. Executive order 9066 i. evacuation of all Japanese Americans ii. set them to (relocation) camps iii. 110,000 of the 127,000 in U.S. moved iv. little or hardly any warning v. lost businesses, homes & possessions vi. could take only what they could carry vii. Hawaii only exception, upset economy d. Japanese did not resist, showed patriotism i. some joined special 442nd infantry combat team a. served only in Europe but toughest fighting b. most decorated unit in the war ii. 1960s Supreme Court ruled lawful in emergency iii. 1990s Congress gave each one interned $20,000 6. Other minorities during the war a. Blacks & Hispanics profit from more employment b. 1942 Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) i. plans march on Washington, D.C. ii. demand end of Jim Crow & equal rights iii. Roosevelt did not want embarrassment iv. stops discrimination in government employment & defense industries but wouldn't desegregate army c. Summer 1943 Detroit race riot i. 25 Blacks & 9 Whites die & state troops stop d. Summer 1943 Zoot Suit Riot in Los Angeles i. military personnel from all over country come to L.A. ii. resentment between military & younger Hispanics iii. after an initial fight the military invaded L.A. a. fleets of taxis came to L.A. with sailors b. the soldiers beat up any young Mexican they saw c. Press blames the youths, even Spanish paper d. Police arrested Mexican youths e. Military finally declared L.A. off limits e. Women found work in better paying jobs i. Roosevelt even allowed women in the armed forces a. most served as nurses, were given commissions b. forbidden to fraternize with enlisted men ii. women doctors entered the war in April 1943 iii. Later in support positions to free men for fighting E. The War 1. U.S. could not concentrate on two fronts at once a. Roosevelt let Japan advance through the Pacific i. Japan controlled almost everything except Australia ii. American & British put in concentration camps b. Germans pushed into Russia almost captured Moscow c. German Africa Corps under Erwin Rommel d. German submarines sank American & British ships 2. Joint effort a. Churchill wanted to postpone invasion and bomb b. Stalin suffered heavy losses and wanted relief c. 1942 Roosevelt calls for invasion in North Africa 3. Roosevelt takes lead a. negotiated with resistance groups i. Gen. Tito-Yugoslavia & Ho Chi Minh-Indochina ii. dealt with Franco for safe passage to Mediterranean b. Roosevelt learnt of Holocaust 11/1942 i. did little to stop it a. only allowed 21,000 Jews to enter U.S. b. won’t bomb gas chambers at Auschwitz ii. Jews in U.S. upset with President's inaction 4. Allied success a.5/ 1942 Battle of the Coral Sea i. prevented invasion of New Guinea & Australia ii. first navel battle that no guns on ships fired iii. battle fought by planes & aircraft carriers proven b. 6/ 1942 the Battle of Midway i. 1st Japanese defeat, a. 4 carriers & over 300 planes c. Island hopping i. Easier to take an island b. Dwight D.Eisenhower across Africa c. July 1943 allies invaded Sicily then headed into Italy i. Italians upset at the loss of Sicily rebelled ii. Hitler took over Italian government & put in Mussolini iii. June 1944 allies capture Rome e. June 6, 1944 Operation Overlord i. combined British & American invasion of Normandy ii. invaded over a month with over 1 million troops f. Industry played a major role i. Germany had better equipment, planes, tanks & rockets ii. Americans better artillery & better trained men a. almost all had mechanical knowledge & used it iii. Americans produced two weapons for every German one g. By 12/1944 victory looked almost complete i. Allied forces marched across Europe and into Germany ii. Just before Christmas Germany launched counter attack a. Battle of the Bulge pushed back allies 50 miles b. Allies over extended with little support c. Eisenhower offered prisoners pardon i. Blacks even allowed to fight h. Victory in Europe i. British distrusted Russians to take Berlin first ii. Eisenhower cuts off retreat to alps a. 5/1945 Hitler commits suicide & 5/8 victory i. Japanese continue to fight i. 1945 Americans start long range bombing of Japan ii. Battle of Ley te Gulf almost destroys Japanese navy iii. Most believed Japanese would fight to last man j. Roosevelt won reelection - new V.P. Harry S Truman k. Yalta Conference February 1945 i. Roosevelt seeks Stalin's help in Pacific & U.N. ii. gave area controlled by Russia in Korea & China iii. They divided Germany & Berlin iv. Russia took part of Poland a. Poland gets part of Germany b. Polish government under USSR v. U.N. charter set for April 1945 in San Francisco a. 50 countries draft charter Roosevelt & dies 4/12/45 l. Potsdam, 7/ 1945 Truman, P.M. Clement Attlee & Stalin i. three cannot agree on dividing Europe ii. 7/16/45 Truman learns of successful Atomic Bomb test iii. They agree to end meeting early and meet again later m. The decision to drop the bomb i. Japanese start kamikaze attacks, loosing war ii. Invasion seemed only option & extremely costly iii. 8/ 6/45 Enola Gay a B-29 dropped bomb on Hiroshima iv. 8/ 9 with no response bombed Nagasaki v. 8/14/45 Japan surrenders to avoid any more bombs