* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Road to War
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Wang Jingwei regime wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
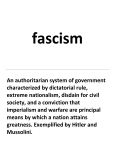
NAME: __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Uses: copy machine, opaque projector, or transparency master for overhead projector. Scholastic Inc. grants teacher-subscribers to Junior Scholastic permission to reproduce this Skills Reproducible for use in their classrooms. Copyright © 2010 by Scholastic Inc. All rights reserved. ® The Road to War The play in our Sept. 6, 2010, issue is set during World War II. (See “We Are Americans Too!” pp. 16-19.) After Japan attacked Pearl Harbor in December 1941, people of Japanese ancestry in the U.S. were seen as security risks. U.S. military leaders urged President Franklin D. Roosevelt to take action. On February 19, 1942, the President signed Executive Order 9066. This led to the removal of an estimated 115,000 Japanese-Americans from their homes. They were forced to live in one of 10 desolate internment camps for the duration of the war. How did World War II begin? The war partly had its roots in the Great Depression, a worldwide economic downturn that began in 1929. The Depression hit Germany and Japan hard. Poverty and unrest in both countries caused democratic governments to fall. They were replaced by dictatorships bent on conquest. Starting in 1931, military leaders gradually took control of Japan’s government. When Japan invaded China in 1937, Roosevelt denounced the Japanese as aggressors. U.S. relations with Japan soon deteriorated. In 1933, Adolf Hitler and his Nazi Party seized control of Germany. Germany attacked Poland in September 1939, starting World War II in Europe. A year later, Germany, Japan, and Italy—another dictatorship— formed an alliance. After studying the chronology, answer the questions. questions skills reproducible READING A CHRONOLOGY CHRONOLOGY July 7, 1937: Fighting breaks out between China and Japan near Beijing, the Chinese capital. Japanese troops soon occupy much of the country. The U.S. supports China against Japan. Dec. 12, 1937: Japanese planes sink the USS Panay, a U.S. gunboat patrolling China’s Yangtze River (now Chang Jiang) under an international treaty. Sept. 3, 1939: Britain and France declare war on Germany in response to the German invasion of Poland. The U.S. proclaims neutrality. June 22, 1940: Overrun by German troops, France surrenders to Hitler. Britain fights on. Dec. 29, 1940: Roosevelt promises to help Britain by making America the “arsenal of democracy.” June 1941: Germany invades the Soviet Union. July 24, 1941: Japanese troops occupy French Indochina (Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Roosevelt freezes all Japanese assets in the U.S. and stops the sale of oil to Japan. Japan’s military calls for war. Oct. 31, 1941: The destroyer USS Reuben James is sunk by a German U-boat in the North Atlantic. Nov. 17, 1941: U.S. and Japanese diplomats start talks to head off war between the two countries. Dec. 7, 1941: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor. The next day, President Roosevelt asks Congress to declare war on Japan. Dec. 11, 1941: Japan’s allies, Germany and Italy, declare war on the U.S. Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. When did World War II begin? 2.Why is the Great Depression seen as one of the causes of World War II? 3. Which three countries formed the Axis alliance? 4. Who led the Nazi party in Germany? 5.Which U.S. warship did the Germans sink on Halloween day in 1941? 6.What did U.S. President Roosevelt do the day after Japan bombed Pearl Harbor? 7.Which two countries started unsuccessful negotiations to head off war in November 1941? 8.What did the U.S. do in response to Japan’s invasion of French Indochina? 9.What event in 1941 prompted the U.S. to relocate Americans of Japanese ancestry? 10.Do you think that President Roosevelt was justified in issuing Executive Order 9066? Give reasons to support your answer. september 6, 2010 • JUNIOR SCHOLASTIC online reproducible