* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Synthetic thyroid hormone T 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
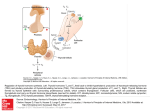
Secretes three hormones essential for proper regulation of metabolism ◦ Thyroxine (T4) ◦ Triiodothyronine (T3) ◦ Calcitonin Located near the parathyroid gland ◦ Which is responsible for maintaining adequate levels of calcium in the extracellular fluid Primary: abnormality in the thyroid gland itself Secondary: results when the pituitary gland is dysfunctional and does not secrete TSH Tertiary: results when the hypothalamus gland does not secrete TRH, which stimulates the release of TSH Cretinism ◦ Hyposecretion of thyroid hormone during youth ◦ Leads to cretinism: low metabolic rate, retarded growth and sexual development, possibly mental retardation Myxedema ◦ Hyposecretion of thyroid hormone during adulthood ◦ Decreased metabolic rate, loss of mental and physical stamina, weight gain, loss of hair, firm edema, yellow dullness of the skin Goiter ◦ Enlargement of the thyroid gland ◦ Results from overstimulation by elevated levels of TSH ◦ TSH is elevated because there is little or no thyroid hormone in circulation Common symptoms ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Thickened skin Hair loss Constipation Lethargy Anorexia Caused by several diseases ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Graves’ disease Plummer’s disease (toxic nodular disease) Multinodular disease Thyroid storm (induced by stress or infection) Affects multiple body systems, resulting in an overall increase in metabolism ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Diarrhea Flushing Increased appetite Muscle weakness Sleep disorders Altered menstrual flow Fatigue Palpitations Nervousness Heat intolerance Irritability levothyroxine (Synthroid, Levothyroidl) ◦ Synthetic thyroid hormone T4 liothyronine (Cytomel) ◦ Synthetic thyroid hormone T3 liotrix (Thyrolar) ◦ Synthetic thyroid hormone T3-T4 combined Thyroid ◦ Desiccated (dried) animal thyroid gland Thyroid preparations are given to replace what the thyroid gland cannot produce to achieve normal thyroid levels (euthyroid) Thyroid drugs work the same way as thyroid hormones To treat all three forms of hypothyroidism Levothyroxine is the preferred drug because its hormonal content is standardized; therefore, its effect is predictable Thyroid replacement in patients whose thyroid glands have been surgically removed Thyroid replacement when thyroid is destroyed by radioactive iodine in the treatment of thyroid cancer or hyperthyroidism Cardiac dysrhythmias are the most significant adverse effect May also cause: ◦ Tachycardia, palpitations, angina, hypertension, insomnia, tremors, headache, anxiety, nausea, diarrhea, menstrual irregularities, weight loss, appetite changes, sweating, heat intolerance, others Radioactive iodine (I131) works by destroying the thyroid gland Surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland ◦ Lifelong thyroid hormone replacement will be needed Antithyroid drugs: thioamide derivatives ◦ methimazole (Tapazole) ◦ propylthiouracil (PTU) Used to palliate hyperthyroidism and to prevent the surge in thyroid hormones that occurs after the surgical treatment or during radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism May cause liver and bone marrow toxicity Assess for drug allergies, contraindications, potential drug interactions Obtain baseline vital signs, weight Cautious use advised for those with cardiac disease, hypertension, and pregnant women During pregnancy, treatment for hypothyroidism should continue Fetal growth may be retarded if maternal hypothyroidism is untreated during pregnancy ◦ Adjust dosage every 4 weeks to keep TSH at the lower end of the normal range Teach patient to take thyroid drugs once daily in the morning to decrease the likelihood of insomnia if taken later in the day Teach patient to take the medications at the same time every day and not to switch brands without physician approval Teach patients to report any unusual symptoms, chest pain, or heart palpitations Teach patients not to take OTC medications without physician approval Teach patients that therapeutic effects may take several months to occur Antithyroid medications ◦ Better tolerated when given with food ◦ Give at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels ◦ Never stop these medications abruptly ◦ Avoid eating foods high in iodine (seafood, soy sauce, tofu, and iodized salt) Monitor for therapeutic response Monitor for adverse effects When assessing the older patient, the nurse keeps in mind that certain non-specfiic symptoms may represent hypothyroidism n older patients, such as: A. Cold intolerance, depression. B. Leukopenia, anemia. C. Loss of appetite, polyuria. D. Weight loss, dry cough. When teaching a patient who has a new prescription for thyroid hormone, the nurse should instruct the patient to notify the physician when which adverse effects are noted? A. Anxiety. B. Appetite changes C. Headache. D. Palpitations