* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Directional Terms - Northside Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
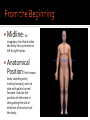
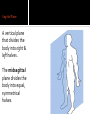
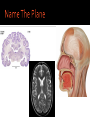
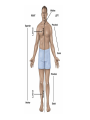
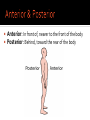
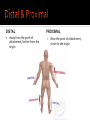
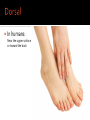
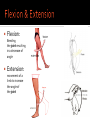
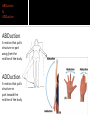
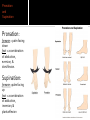
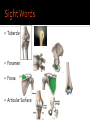
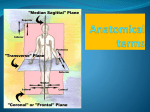
Human Anatomy Midline: An imaginary line that divides the body into symmetrical left & right halves Anatomical Position: the human body standing erect, looking forward, arms at side with palms turned forward. Used as the position of reference in designating the site or direction of structures of the body. Dividing the body into halves Sagittal Plane A vertical plane that divides the body into right & left halves. The midsagittal plane divides the body into equal, symmetrical halves. Transverse Plane A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior & inferior halves Coronal Plane A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior & posterior halves. The coronal plane is also know as the frontal plane. Used to describe the locations of structures in relation to other structures or locations in the body. Anterior: In front of, nearer to the front of the body Posterior: Behind, toward the rear of the body DISTAL Away from the point of attachment, farther from the origin PROXIMAL Near the point of attachment, closer to the origin Superior: Above, over, situated more towards the head & away from the feet Inferior: Below, under, situated below & closer to the feet Lateral: Toward the side, away from the midline Medial: Toward the midline, away from the side, middle Superficial: Toward or on the surface of a structure; outward Deep: Away from the surface, further into the body; inward Relating to or involving the palm of the hand Relating to or involving the sole of the foot In humans: Near the upper surface or toward the back Of or relating to the belly, abdominal. Located on, or toward the front part of the human body Lying on the stomach, face down Lying on the back, face up Ipsilateral: on the same side of the body as another structure Contralateral: on the opposite side of the body from another structure Bilateral: pertaining to, involving, or affecting two or both sides Unilateral: relating to, or affecting one side How a joint moves Flexion: Bending the joint resulting in a decrease of angle Extension: movement of a limb to increase the angle of the joint ABDuction & ADDuction ABDuction: A motion that pulls a structure or part away from the midline of the body ADDuction: A motion that pulls a structure or part toward the midline of the body Internal Rotation: flexed inwards towards the midline External Rotation: flexed outwards away from the midline Pronation and Supination Pronation: forearm = palm facing down foot = a combination of abduction, eversion, & dorsiflexion. Supination: forearm =palm facing up foot = a combination of adduction, inversion, & plantarflexion Tubercle Foramen Fossa Articular Surface