* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise of Mussolini in Italy
Romano Romanelli wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Comparison of Nazism and Stalinism wikipedia , lookup
Austrofascism wikipedia , lookup
José Antonio Primo de Rivera wikipedia , lookup
Giovanni Gentile wikipedia , lookup
Florestano Di Fausto wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Italy wikipedia , lookup
Robert Soucy wikipedia , lookup
Gabriele D'Annunzio wikipedia , lookup
Benito Mussolini wikipedia , lookup
Italian Empire wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Anti-fascism wikipedia , lookup
Italian Fascism wikipedia , lookup
Italian Social Republic wikipedia , lookup
National Fascist Party wikipedia , lookup
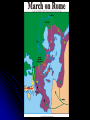
Quick Write What are the differences and similarities between Fascism and Communism? Fascism in Europe What is Fascism? A political movement that promotes an extreme form of nationalism, a denial of individual rights, and dictatorial one party rule. Mussolini Mussolini Why Fascism? Many European countries saw fascism, communism, and dictatorship as the only way to survive the economic problems and instability. Communism vs. Fascism Communism Promote a classless society One supreme leader Goal: Spread of communism worldwide Karl Marx Fascism Allow for different classes to emerge Goal: Devotion to one’s country (NATIONALISM) The wills of the country over the people Quick Write What societal conditions do you think there were that allowed for these Totalitarian regimes to rise in the 1st half of the 20th century. Quickly describe how they came to power. The Rise of Mussolini in Italy Benito Mussolini (1883-1945) What you will learn: 1.) You will learn the conditions of Italy after WWI that made it ripe for a totalitarian takeover. 2.) You will reinforce your knowledge of fascism. 3.) You will learn about how Benito Mussolini arose to power. 4.) You will learn about his reign as dictator of Fascist Italy. 5.) You will learn about the beginning of the role he played in WWII. 6.) You will learn about Mussolini’s influence on Italian society and the world. Problems after WWI for Italy 460,000 soldiers killed Heavy debt (wars are expensive) Britain and France did not give Italy the land they promised in Treaty of London This is what got Italy to switch sides Gv’t of Italy at the time was bad Rising unemployment The Treaty of Versailles Italians believed that the T of V had treated them poorly. Italy had not been given the land promised at the Secret Treaty of London. Italy’s foreign Minister Orlando left before the conference ended, feeling humiliated. Who are these men? What is fascism? A system of government under a dictator. Strong support of the nation over the individual!! Usually involves terror, censorship, nationalism, and racism. How does this represent fascism? Benito Mussolini Mussolini began his career as a journalist where he started to gain his own ideas in what became known as Fascism. Mussolini gains power Mussolini set up a Fascist Party and promised to solve Italy’s problems WHY DOES THIS SOUND FAMILIAR?? Promised to rebuild Italy and recreate the Roman Empire Organized armed gangs called the “Blackshirts” Blackshirts: Supporters of Mussolini Mussolini Came to power in 1922 and was appointed Prime Minister by King Victor Emmanuel to prevent a Communist Revolution in Italy Why would King Victor Emmanuel want to stop a Communist Revolution? How does putting Mussolini in charge accomplish this? 1922 March on Rome to establish Mussolini and the Fascist Party as the most important party in Italy Mussolini said this at a party conference: "Either the government will be given to us or will shall seize it by marching on Rome." Seizure of Power Mussolini’s capture of power In October 1922, 30,000 fascists marched on Rome, threatening King Victor Emmanuel III to give Mussolini the power. The king did not love the former liberal politicians, so he agreed to give Mussolini the power March on Rome, 1922 His leadership Mussolini became Il Duce (ihl Doo-chay), meaning the leader. He enforced fascism throughout his country. He forced all the other political parties to be illegal and he also got rid of the democracy. His opponents were put to jail by his secret police. The government took control of all the radio stations and all the other Medias to broadcast only the doctrines of the fascism. Fascism under Mussolini A couple of quick questions Do you think people were upset by Mussolini creating a fascist state Italy? I mean Mussolini is restricting freedom, he is terrorizing people through his secret police? Most of the Italians in the 1920s30s supported Mussolini and his fascist state!! How do you think Mussolini was able to gain and maintain this much support? Government by Propaganda One of the reasons why Mussolini was able to gain support from the people was the through use of propaganda. Propaganda = message such as posters made to convince people’s mind, sometimes with lies Mussolini “Controlled Media” Mussolini and his government controlled all the multi-medias including radio, press, newspaper and education to force people to think that fascism was the right and the best doctrine. (C in SCOOP: Controls…) Propaganda was also used to ensure the national spirit for the people in Italy and remind people how powerful Mussolini was. Propaganda Posters The poster on the far right shows the slogan by Mussolini. It says, “Believe, Obey, Fight”. Schools taught these 3 discipline to the students. More Propaganda Mussolini and Hitler Mussolini was outcast from the League of Nations. (WHAT IS THE LEAGUE OF NATIONS?) Mussolini and Hitler In October 1936 they signed a non-military alliance. Mussolini signed a full defensive alliance with Nazi Germany in the Pact of Steel. Italy during WWII Mussolini intended to annex Malta, Corsica, and Tunis. He wanted to create a “New Roman Empire.” He annexed Albania, straining the military. His troops were unprepared for the German invasion of Poland. Italy remained neutral. Mussolini during WWII Spain Spanish Civil War (1936-1939) Republicans vs. Nationalists/Fascists Germany and Italy supported the Nationalists Russia and many international brigades supported the republicans. Abraham Lincoln brigade from the United States. The nationalists won. Francisco Franco became the fascist dictator. Guernica by Pablo Picasso Painted in 1937 in response to the German bombing of the Spanish city of Guernica in support of Francisco Franco's Fascist forces. It shows the tragedies of war and the suffering it inflicts upon individuals, particularly innocent civilians. Nazism Totalitarianism Communism Fascism *These theories, specifically Communism and Fascism, are completely different theories that are bitterly opposed; however they exhibit the same behavior I am Joseph Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union from 1922-1953. What is Communism? • LEFT WING • based on theory by Karl Marx • revolutionary idea of a political, economic and social system that creates a “classless society” • state ownership and control of the means of production (no private ownership) • Soviet Communism or “Stalinism”, was more of a totalitarian and military state combined with elements of communism I am Benito Mussolini the leader (Il Duce) of Italy from 1922 to 1943. What is Fascism? • RIGHT WING • intense nationalism and elitism • totalitarian control • interests of the state more important than individual rights • maintain class system and private ownership Interesting Fact: Fascism name was derived from the fasces, an ancient Roman symbol of authority consisting of a bundle of rods and an ax I am Adolf Hitler the leader (der Fuhrer) or dictator of Germany from 1933 to 1945. What is Nazism? • extremely fascist , nationalistic and totalitarian • based on beliefs of the National Socialist German Workers Party • belief in the racial superiority of the Aryan, the “master race” • belief that all Germans should have “lebensraum” or living space in Europe •Violent hatred towards Jews and blamed Germany’s problems on them