* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Page 93 Static electricity is the buildup of electric charge on an
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
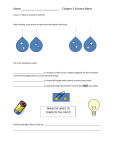
Page 91 S8P5. Electricity What is electricity and how is static electricity different from “regular” electricity? Most matter does not have an overall charge (# of protons = # of electrons) At times, matter can become charged either positively or negatively. If an object has more protons, it is positively charged. If an object has more electrons, it is negatively charged. These are called ions. Objects can become charged by friction. When objects made up of two different materials rub against each other, the electrons from one object can move to the other object. On page 90 – Write the question and answer Imagine you are doing an experiment with static electricity. You have a negatively charged balloon and a plastic comb. You do not know whether the comb is positively or negatively charged. What can you do to determine the charge on the comb? Page 93 Static electricity is the buildup of electric charge on an object. Examples: balloon rubbed against hair or clothes tumbling in a dryer. Static electricity can be discharged or released slowly over time. Clothes with static electricity will eventually lose their charge over time because these charges will move to the water molecules in the air. If you pull apart clothes stuck together by static electricity, static electricity is discharged quickly (this is the crackling sound you hear) Charged particles can exert forces on other charged objects. The force between charged particles is called electric force. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract. On page 92 – Write the questions and answers under each. The protons in an atom are in the nucleus. The electrons of the atom move around the nucleus. What keeps the electrons from moving away from the nucleus? If you charge a balloon by rubbing it on your hair and then put the balloon against a wall, the balloon will stick to the wall. The charge on the balloon induces a positive charge on the wall and an electric force between the balloon and wall causes the balloon to stick. If you leave the balloon alone, it will eventually fall off the wall. Explain why. Page 95 Electric charges do not always stay built up on objects. Electric current is a flow of electric charges through matter, and the rate that the charges pass a given point. Electric currents can transfer electrical energy to power devices such as televisions and computers. Electric current (I) is measured in the units amperes or amps (A). The amount of current flowing in a wire depends on voltage and resistance. Voltage is a measure of the potential energy per unit charge and is measured in the unit of volts (V). Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric charge and is measured in the unit of ohms () Summary: EQ- What is electricity and how is static electricity different from “regular” electricity? Page 97 S8P5. Electricity What are the advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel circuits? Some materials have low resistance and conduct electric current well. These are called conductors and are often used to make wires. Examples of conductors are copper, gold, silver, tin, lead, etc. Other materials have a resistance that is so high that hardly any charges can flow through them. Materials that do not conduct electric current well are called poor conductors or insulators. Examples of insulators are glass and diamonds. On page 96 – Create a 2 column table and categorize the following materials as conductor or insulator. Gold, silver, plastic, glass, wood, leather, tin, aluminum, lead, platinum, ceramic, cloth, copper Conductor Insulator Page 99 In solid conductors, the movement of electrons carries the current. Current flows in wires and in electric devices when the wires and devices are connected in a complete closed path called a circuit. All circuits contain three basic parts: an energy source, a load and wires. The energy source provides the voltage that causes charges to flow as a current. Ex. battery A load is a device in a circuit that changes electrical energy into other kinds of energy. Ex. lightbulb The wires of a circuit are used to connect energy sources to loads. Circuits may have several loads and many wires, but often only have one energy source. On page 98 – Create a 3 column table and categorize the following materials as an energy source, load or wire (material for wire) Battery, lightbulb, copper, gold, radio, electric generator, solar energy cells, silver, tin Energy Source Load Wire material Page 101 There are two basic types of circuits: series and parallel. Loads connected together in a single loop are called a series circuit. Because a series circuit is a single loop, any break in the circuit will cause the current to stop its flow. Loads connected side by side are a parallel circuit. In a parallel circuit, there are multiple loops because each load is in its own loop. Because each load is in its own loop, the circuit will continue to allow the current to flow is one of the loops is broken. Summary: EQ- What are the advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel circuits? On page 100 – Draw a series and a parallel circuit each with 3 loads. Label all the major parts and describe what will happen if one load fails in each of the circuits. Page 103 S8P5. Magnetism What are the differences between permanent magnets and electromagnets? A magnet is a material that exerts an attractive force on certain other materials. Magnets are made of elements such as iron, nickel or cobalt. A magnetic force is a push or pull that is exerted by a magnet. A magnet has two poles: a north pole and a south pole. Each pole exerts a magnetic force. If the poles are alike, the poles repel (push away). If the poles are different, they will attract (pull towards each other). The area surrounding a magnet in which the magnetic force exists is called the magnetic field. On page 102 Like poles repel or push away S N N S Opposite poles create an attractive force. S N The magnetic field of a bar magnet. The field is represented by lines that extend from one pole of the magnet to the other. The lines are closest together at the poles of the magnet. This is the region where the magnetic force is strongest. The magnetic forces are weaker near the center of the magnet where the lines are farther apart. S N N S Page 10 The production of a magnetic field by electric current is called electromagnetism. A magnet that is made by passing an electric current through a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is called an electromagnet. Electromagnets are useful devices because their magnetism can be turned on and off. They are also useful because the strength of the magnetic field can be controlled. This can be accomplished in three ways: by changing the amount of current flowing through the wire, by adding or removing coils of wire, or by changing the size of the iron core of the electromagnet. On page 104 Changing the Strength of an Electromagnet To Increase Strength To Decrease Strength Increase strength of current Decrease strength of current Add more coils Use fewer coils of wire Increase size of iron core Decrease size of iron core Page 107 An electric motor is a device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electromagnets are used in any device that contains a generator. A generator is a device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy. Summary: EQ- What are the differences between a permanent magnet and a temporary magnet? Page 109 S8P2. Thermal Energy What is the difference between thermal energy, heat and temperature? Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of all particles in a substance. The thermal energy of a substance depends on two factors: the temperature of the substance and how much substance there is. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of all the particles in a substance. When the motion of a substance changes, the temperature changes too. The faster the particles move, the higher the temperature. The slower the particles move, the lower the temperature. Page 11 Thermal energy and temperature are closely related , but they are not the same. Temperature is an average. It does not depend on the amount of particles. Heat is the flow of thermal energy. Heat always moves from an area of higher temperature to an area of lower temperature. It will flow this way until all materials are the same temperature. Heat can be transferred in 3 ways: conduction, convection and radiation. Page 113 Conduction is the transfer of heat by direct contact of particles. Ex. frying an egg Convection is the transfer of heat in fluids (including gases) by the movement of currents. Ex. boiling rice Radiation is the transfer of heat without matter. Ex. sun shining Conduction and convection require matter, radiation does not require matter. Summary: EQ- What is the difference between thermal energy, heat and temperature?