* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pop-Quiz Sit down quietly and draw the following structures.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
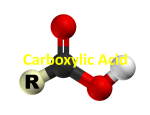
Pop-Quiz Sit down quietly and draw the following structures. Pop-Quiz Draw the following structures: Heptan-2-ol Cyclopropanal 1-propoxypentane Heptan-3-one 2,4,6-trichloroheltanal Nomeclature: Carboxylic acids and Esters Structure of carboxylic acids and their derivatives • The functional group present in a carboxylic acid is a combination of a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group; however, the resulting carboxyl group ( -COOH) possesses properties that are unlike those present in aldehydes/ketones and alcohols. carbonyl group hydroxyl group carboxyl group Structure of carboxylic acids and their derivatives • Carboxylic acids have the following general formula: • Some simple carboxylic acids: formic acid IUPAC: methanoic acid acetic acid IUPAC: ethanoic acid IUPAC: benzoic acid • Since carbon can have only four bonds, there are no cyclic carboxylic acids (i.e. the carboxyl group cannot form part of a carbon ring) IUPAC nomenclature for carboxylic acids • For monocarboxylic acids (one –COOH group): – Select the longest, continuous carbon chain that involves the carboxyl group. This is the parent chain and the –COOH carbon is designated as C-1. – Name the parent chain by dropping the “e” from the corresponding alkane name and changing to “oic acid” – Indicate the identity and location of substituents on the parent chain at the front of the carboxylic acid’s name Benzoic acid Butanoic acid 3,3-Dibromobutanoic acid 2-Methylpropanoic acid 3,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid IUPAC nomenclature for carboxylic acids • Dicarboxylic acids: – For these compounds, both ends of a chain will end with a –COOH group. The parent chain is the one that involves both –COOH groups. – The parent chain is named as an alkane and the term “dioic acid” is added afterwards to indicate the diacid structure. Butanedioic acid (Succinic acid) Bromobutanedioic acid Bromosuccinic acid) Common names for carboxylic acids Common names for dicarboxylic acids Common names for carboxylic acids • For common-name carboxylic acids and diacids, substituents are often numbered using a Greek system: Greek letter carbon number 5 4 3 2 1 • So the following molecule is called 2-Methylpropanoic acid. Polyfunctional carboxylic acids • Carboxylic acids that contain other functional groups besides the –COOH group are called polyfunctional carboxylic acids. Some examples are shown below: an unsaturated acid a hydroxy acid a keto acid Task 2 Give IUPAC names for the following: A. CH3COOH CH3 | B. CH3CHCOOH 12 Solution 2 A. CH3COOH ethanoic acid CH3 | B. CH3CHCOOH 2-methylpropanoic acid; 13 Physical properties of carboxylic acids • Carboxylic acids are the most polar functional group we have seen so far. The presence of the carbonyl group next to the OH causes the O-H bond to be even more polar. alcohols carboxylic acids Physical properties of carboxylic acids • Because of the very polar –COOH group, carboxylic acids exhibit strong intermolecular attractions. • As expected, carboxylic acids of a given number of carbon atoms have higher boiling points than alcohols. • Carboxylic acids also tend to dimerize, producing molecules that are twice as heavy which have enhanced London forces (and thus still higher boiling points). two H-bonds between two molecules "dimer" Comparing Boiling Points Physical properties of carboxylic acids • In terms of water-solubility, because of H-bonding, carboxylic acids dissolve well in water (up to 4-carbon chains). • Beyond 4 carbons, water-solubility drops off rapidly. Structure of esters • Esters are carboxylic acid derivatives having an alkoxy group instead of a hydroxyl group. carboxylic acid ester Nomenclature for esters • Thinking of an ester in terms of an “alcohol portion” and a “carboxylic acid portion” is important for naming esters using the IUPAC system: 1. The name for the alcohol portion comes first: name the alkyl part of the alcohol (e.g., for the ester shown below, the first part of the ester’s name is methyl (alcohol part comes from methanol). Present the alkyl name separate from the remainder of the ester name. 2. The carboxylic acid portion is named as if it were deprotonated, changing the “-ic acid” part of that name to “-ate” Methyl propanoate derives from derives from propanoic acid methanol This part would be called “propanoate” Nomenclature for esters • Some other examples: Ethyl butanoate Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate Ethyl -methylbutyrate 2-Methylpropyl butanoate Isobutyl butanoate 2-Butyl butanoate Sec-Butyl butanoate Selected common esters • Flavor/fragrance agents Selected common esters • Pheromones: alarm pheromone for honeybee sexual attractant for canines • Medications: benzocaine Aspirin Selected common esters • Synthesis of Aspirin H+ H2O heat salicylic acid Aspirin acetic acid • Synthesis of oil of wintergreen: H+ Methanol H2O heat Aspirin salicylic acid Task 2 Give the IUPAC name of the following compound, which is responsible for the flavor and odor of pears. O CH3 — C—O —CH2CH2CH3 24 Solution 2 O propyl CH3 — C—O —CH2CH2CH3 propyl ethanoate (IUPAC) 25 Isomerism in carboxylic acids and esters • Recall that structural isomers are molecules that share the same formula but differ in their atom-to-atom connectivities. • Carboxylic acids and esters that have a given number of carbon atoms form another example of functional group isomers: functional group isomers Butanoic acid C4H8O2 Methyl propanoate Physical properties of esters • Because they don’t possess OH groups, esters cannot form Hbonds with other ester molecules. As a result, esters have lower boiling points than carboxylic acids and alcohols that have approximately the same molar mass. • Water molecules can H-bond to esters, at the oxygen atoms. This makes low molecule weight esters water-soluble. Task 3 Draw the structure of the following compounds: A. 3-bromobutanoic acid B. Ethyl propionoate 28 Solution 3 A. 3-bromobutanoic acid Br | CH3CHCH2COOH B. Ethyl propionoate O CH3 CH2 COCH2CH3 CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 29