* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 250 - WordPress.com
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
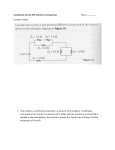
Physics 300 Unit Review: Circuitry Mr. Youker | You are to complete this Homework Assessment through the use of your text, notes, and brain. You are not to receive aid on this assignment from your classmates, friends, teachers, or other similar source. Answer all questions completely on a separate piece of paper. 1. A simple circuit consists of two resistors (5 Ω, 15 Ω) placed in series with a 9.0 V battery. a. Produce a schematic diagram of this circuit, including both resistors and the battery. b. Calculate the net resistance of the circuit. c. Calculate the amount of current passing through each resistor. d. Calculate the voltage (∆V) across each resistor. e. Add a voltmeter to your diagram, making it measure the ∆V of one of the resistors. 2. A simple circuit consists of two resistors (30 Ω, 15 Ω) placed in parallel with a 9.0 V battery. a. Produce a schematic diagram of this circuit, including both resistors and the battery. b. Calculate the voltage (∆V) across each resistor. c. Calculate the amount of current passing through each resistor. d. Calculate the net resistance of the circuit. e. Add an ammeter to your diagram, making it measure the current in one of the resistors. 3. A complex circuit consists of a 20 Ω and a 10 Ω resistor placed in series with one another. A 40 Ω resistor is then placed in parallel with only the 20 resistor. An ammeter registers the current through the 20 Ω resistor to be 6.0 A. A battery supplies a voltage to the whole circuit. a. Produce a schematic diagram of this circuit, including all three resistors and the battery. b. Calculate the amount of current passing through each resistor. c. Calculate the voltage (∆V) across each resistor and the total voltage. d. Determine the power delivered by the 10 Ω resistor. e. If the 40 Ω resistor were to be removed, would the power delivered by the 10 Ω resistor increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain. 4. Determine the net resistance of this circuit: Each resistor ( 5. Sketch the circuit and fill in the missing information: A circuit consists of two series resistors (R1, R2) with a parallel branch (R3) around both R1 and R2. Battery EMF: 180 V R1 = V1 = R2 = V2 = V3 = R3 = Diagram: 90 Net Current: 10 A ) is 100 Net Resistance: 32 V I1 = A P1 = W V I2 = A P2 = W V I3 = A P3 = W