* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BROMELIACEAE
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
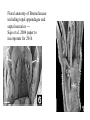
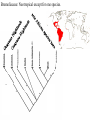
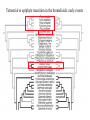
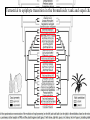
BROMELIACEAE Epiphyte life form of the bromeliads - Mexico Epiphyte life form of the bromeliads Bromelia perianth Bromeliaceae monocots Current Angiosperm Phylogeny Group Tree for Flowering Plants Poales BROMELIACEAE (POALES, MONOCOTS) NUMBERS: 46 Genera, 2110 species GEOGRAPHY: tropical (and subtropical) America (one species, Pitcairnia feliciana, in tropical west Africa) HABITAT: prominent epiphytes, but also terrestial plants CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC OF MONOCOTS: herbaceous, sympodial plants; vascular bundles in stem scattered, closed [no interfascicular cambium developing]; tertiary veins without free endings, leaf base sh eathing; pollen monosulcate, gynoecium three-parted; cotyledon 1; primary root present but unbranched, not persisting. CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC OF FAMILY: Habit: rosette herbs and he rbs (rarely rosette trees and climbers) Shoot often reduced (internodes extremely short) Vessels throughout plant (missing from roots of some epiphytes, wh ich use peltate hairs on surface for water transport) Leaves spiral (vs. distichous), with broad sheathing base often seving as water trap; terrestrial species usually spiny-edged Indument includes wa ter-absorbing peltate scales sunk in ep idermal pit. Crystalline Inclusions: sacs of calcium oxalate raphides abundant in all parts; spherical silica bodies in leaf and stem epidermis Inflorescence terminal racemes often with bright-colored bracts (continuing shoots sympodial=axillary as in most monocots) Flowers bisexual, mostly radially symmetrical Perianth 3 + 3 tepals, more or less differentiated, usually tubular (but not fused) Stamens 3 + 3 (connate or not, adnate to tepals or not) Gynoecium 3-carpellate, 3-locular, with septal nectaries; many seeds with helobial endosperm Pitcairnioideae (capsules, seeds without hairs) Floral anatomy of Bromeliaceae including tepal appendages and septal nectaries --Sajo et al. 2004 paper to incorporate for 2016 Pitcairnia Neoregelia flowers sessile in center Al Gentry photo Walter Judd photo Tillandsioideae (capsules, seeds with hairs) Tillandsia with inflorescence Tillandsia - typical habit (Chiapas, Mexico) Tillandsia usneoides Tillandsia as decoration, Chiapas, Mexico Vriesia sintenisii Walter Judd photo Bromelioideae (berries) Fig 1 (more Tillandsoideae, Fig. 2) The pineapple - terrestrial, leaves with spines, fleshy fruits, inferior ovary, and delicious. Ananas bracteatus, an ornamental BROMELIACEAE: MORPHOLOGY AND MOLECULES 1 -superior ovary , fruits dry, seeds tailed 2 - superior ovary, fruits dry, seeds comose 3 - inferior ovary, fruits fleshy, seeds without appendages 1 1 2 1 1 3 1 1 Bromeliaceae: Neotropical, with the ealiest-diverging species in the Guayana Highlands Brocchinia and Lindmania from the Guayana Highlands currently stands as most primitive bromeliad Bromeliaceae: Neotropical except for one species. Pitcairnia feliciana from West Africa – the only Old World bromeliad Terrestrial to epiphyte transition in the bromelioids: early events Puya Andes- Costa Rica Bromelia - habit and fruiting axis Santa Rosa, Costa Rica The pineapple - terrestrial, leaves with spines, fleshy fruits, inferior ovary, and delicious. Ananas bracteatus, an ornamental Terrestrial to epiphyte transition in the bromelioids: tank and sepal cha Aechmaea- beautiful, artificial